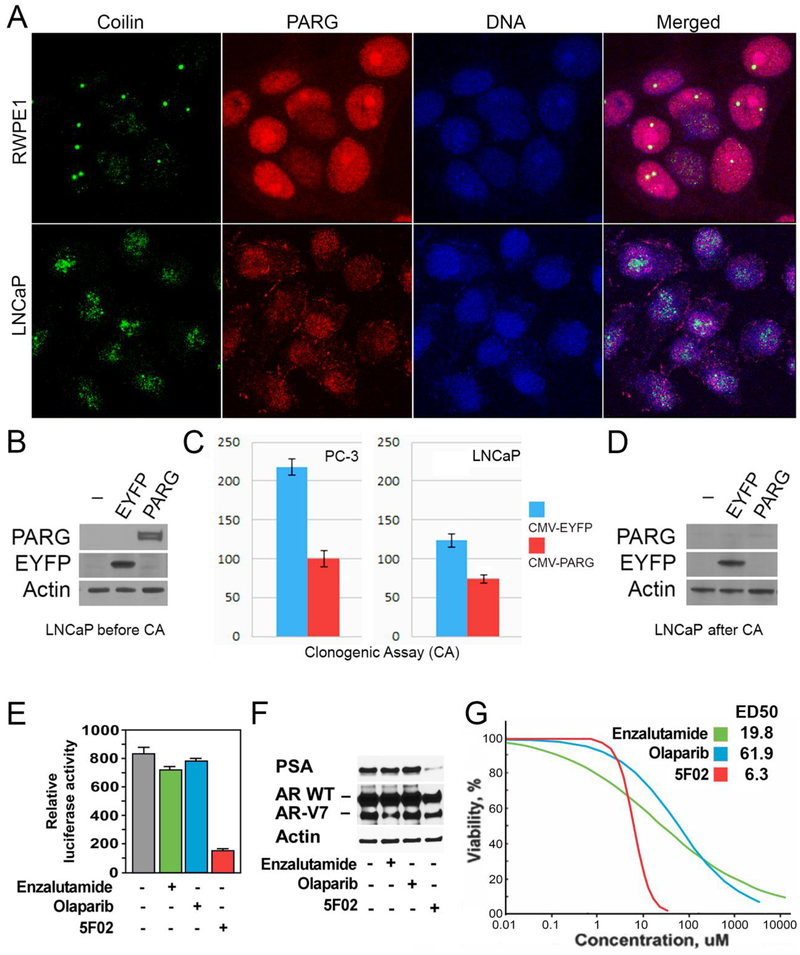
Figure 3. Non-NAD-like PARP-1 inhibitors suppress malignant phenotype of prostate cancer cells.
A. The morphology of Cajal bodies (CBs) in disrupted in PC cells. Normal prostate cells (RWPE1), prostate cancer cells (LNCaP), were fixed and immunostained with rabbit anti-PARG (Red) and Guinea Pig anti-Coilin antibody (green). Nuclear DNA were detected with the Draq5 dye (blue). The disruption of CBs in cancer-derived cells is clearly visible. B-D. LNCaP PC cells were transfected with plasmids expressing EYFP or the PARG proteins under control of CMV promoters. After cell amplification, we examined the levels of ectopic proteins expression, using Western blot analysis (B). We compared the malignant potential of EYFP and PARG expressing cells using Clonogenic Cell Survival Assay (C). After that, we retested the level of ectopic proteins expression in cells growing on plates (D). E-F. The effects of 5F02, olaparib, and enzalutamide on the AR transcriptional activity in LNCaP cells expressing both wild-type and constitutively active AR spliced variant AR-V7. LNCaP cells stably expressing AR-V7 and firefly luciferase driven by AR-dependent promoter were treated with the indicated agents for 8 hrs. Samples were assayed for firefly luciferase activity (E). LNCaP cells stably expressing AR-V7 were treated with 5F02, olaparib, or enzalutamide (all at 10μM) for 24 hrs. PSA and AR levels were examined by Western blot analysis (F). G. The effect of 5F02, olaparib, and enzalutamide on viability of LNCaP expressing both wild-type and constitutively active AR splice variant AR-V7. Cells were treated with escalating concentrations of each of the three inhibitors for 96 hours. Cellular viability was assessed using the CellTiter Blue assay. The effective doses (ED) were calculated using XLfit software and presented in Table 1.