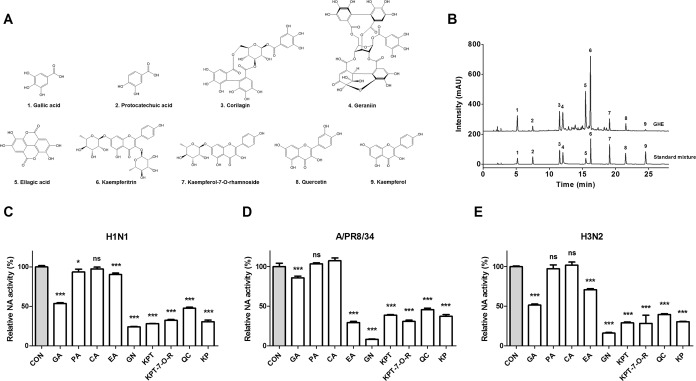
Figure 3.
The HPLC profile of the components in GHE was monitored at 265 nm and compared with that of nine standard compounds. (A) Structures of the nine components of GHE: 1, Gallic acid; 2, Protocatechuic acid; 3, Corilagin; 4, GN; 5, Ellagic acid; 6, Kaempferitrin; 7, Kaempferol-7-O-rhamnoside; 8, Quercetin; 9, Kaempferol. (B) HPLC profile of 5 mg/mL GHE and standard compounds. Measurement of the antiviral activity of GHE components (100 μM) using neuraminidase inhibition assay. The influenza A viruses H1N1 (C), A/PR/8/34 (D), and H3N2 (E) were added to the indicated concentrations of GHE components. Fluorescence was measured using fluorescence spectrophotometry (excitation, 365 nm and emission, 415–445 nm). Bar graph (mean ± SEM) statistics were determined by three experiments’ data using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, ***P < 0.001; *P < 0.05, compared with the CON (GHE untreated) samples. GA, Gallic acid; PA, Protocatechuic acid, CA, Corilagin; GN, Geraniin; EA, Ellagic acid; KPT, Kaempferitrin; KP-7-O-R, Kaempferol 7-O-rhamnoside; QC, Quercetin; KP, Kaempferol.