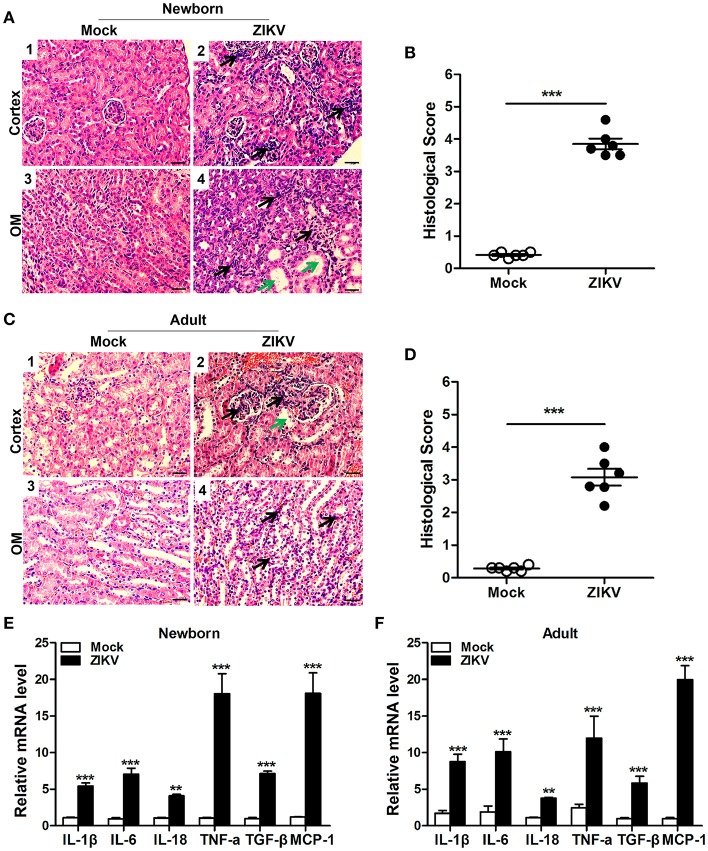
Figure 4.
ZIKV infection increased inflammatory cell infiltration and cytokines expression in the kidneys. (A–D) Morphological changes and quantification of histological damage in the cortex and outer medulla (OM) of newborn (A) and adult (C) mouse kidneys at 14 days post-infection. Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (scale bar: 20 μm); green arrows in the images indicated cell vacuolization; black arrows indicated inflammatory cell infiltration. (B–D) The histological score of newborn mice (B) and adult mice (D) were determined by tubular dilatation, vacuolization, tubular cell necrosis, loss of brush border, interstitial edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration. (E,F) The relative mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, TNF-α, TGF-β, and MCP-1 in the kidneys of mock and ZIKV-infected newborn (E) and adult (F) mice at 7 days post-infection were determined by qRT-PCR. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6), **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. mock group.