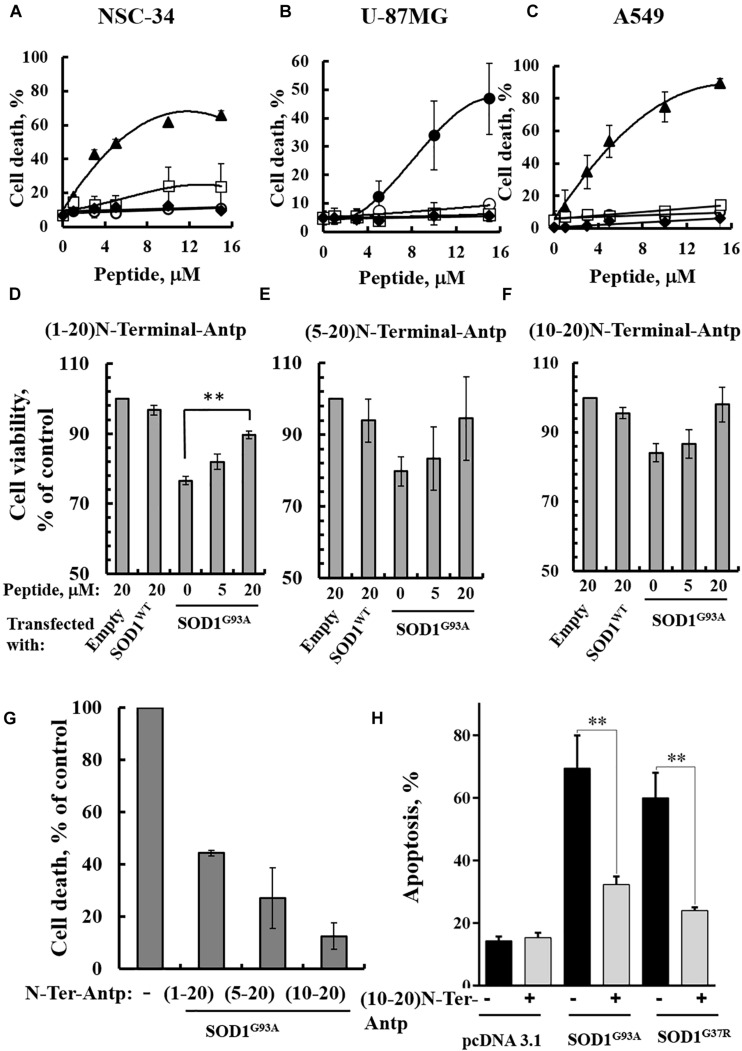
FIGURE 4.
VDAC1 N-terminal peptides inhibit the cell death of NSC-34 cells mediated by mutant SOD1G93A. NSC-34 (A), U-87MG (B), or A549 (C) cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of (1-26)N-Ter-Antp (∙), D-(15-26) (19-26)N-Ter-Antp (▲), (1-20)N-Ter-Antp (∘), (5-20)N-Ter-Antp (□) or (10-20)N-Ter-Antp (◆) peptide for 5 h. Cell death was analyzed using PI staining and flow cytometry. (D–F) NSC-34 cells were transfected to express human SOD1WT, the human mutant SOD1G93A, or neither (empty), in each case either without or with addition of increasing concentrations of the indicated VDAC1 N-terminal-derived peptide for 5 h. Cell viability analysis was performed with the CellTiter 96 AQueous one-solution cell proliferation assay with ELISA at 490 nm. (G) The rescuing effects of the VDAC1 N-terminal-derived peptides are shown as a percentage of cell death. The significance of quantitative analysis of triplicates of different biological repeats (n = 3) was performed by Student’s t-test; ∗∗P < 0.01. (H) SH-SY5Y cells (4.5 × 104 cells/well in 24-well plates) were transfected with an empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding for mutant SOD1G93A or SOD1G37R. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, the cells were incubated for 5 h with (10-20)N-Ter-Antp peptide (20 μM) and then analyzed for apoptosis using acridine orange and ethidium bromide staining, as described previously (McGahon et al., 1995). Fluorescence microscopy images were analyzed and about 100 to 300 cells were counted for each treatment in representative microscopic fields. The significance of quantitative analysis of triplicates of different biological repeats (n = 3) was performed by one-way Anova; ∗∗P < 0.01.