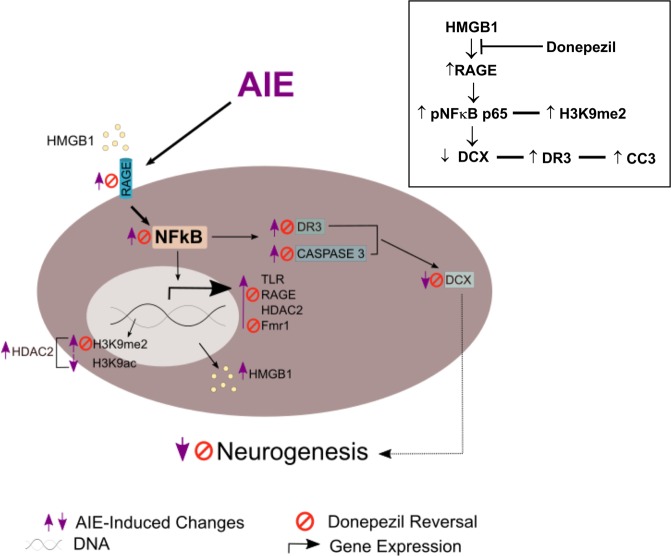
Figure 8.
Hypothetical model of AIE-induced adult pathology and the mechanisms of Donepezil reversal of AIE effects. AIE increases expression of adult hippocampal HMGB1 and RAGE consistent with increased signaling of this agonist-receptor combination. HMGB1-RAGE increases pNFκB transcription of RAGE feeding forward to enhance expression of DR3, which, in turn activates cell death caspase cascades as indicated by increased active caspase 3, the executioner caspase. RAGE is expressed on DCX + IR neuroprogenitors consistent with RAGE increasing DCX cell death that contributes to the persistent loss of neurogenesis after AIE. AIE increases RAGE, pNFkBp65 and increases H3K9me2, an epigenetic marker of gene silencing. Gene silencing involves histone methylation of H3K9me2 and is reciprocal with deacetylation, the loss of H3K9ac. HDAC2 is increased in neurons by NFkB consistent with reduced BDNF in response to RAGE-NFkB activation. Donepezil reversed RAGE, pNFkBp65, H3K9me2, DR3, caspase-3 and loss of DCX after AIE. These findings are consistent with an anti-inflammatory action of donepezil either through increasing acetylcholine and/or through anti-inflammatory microglial inhibitory mechanisms.