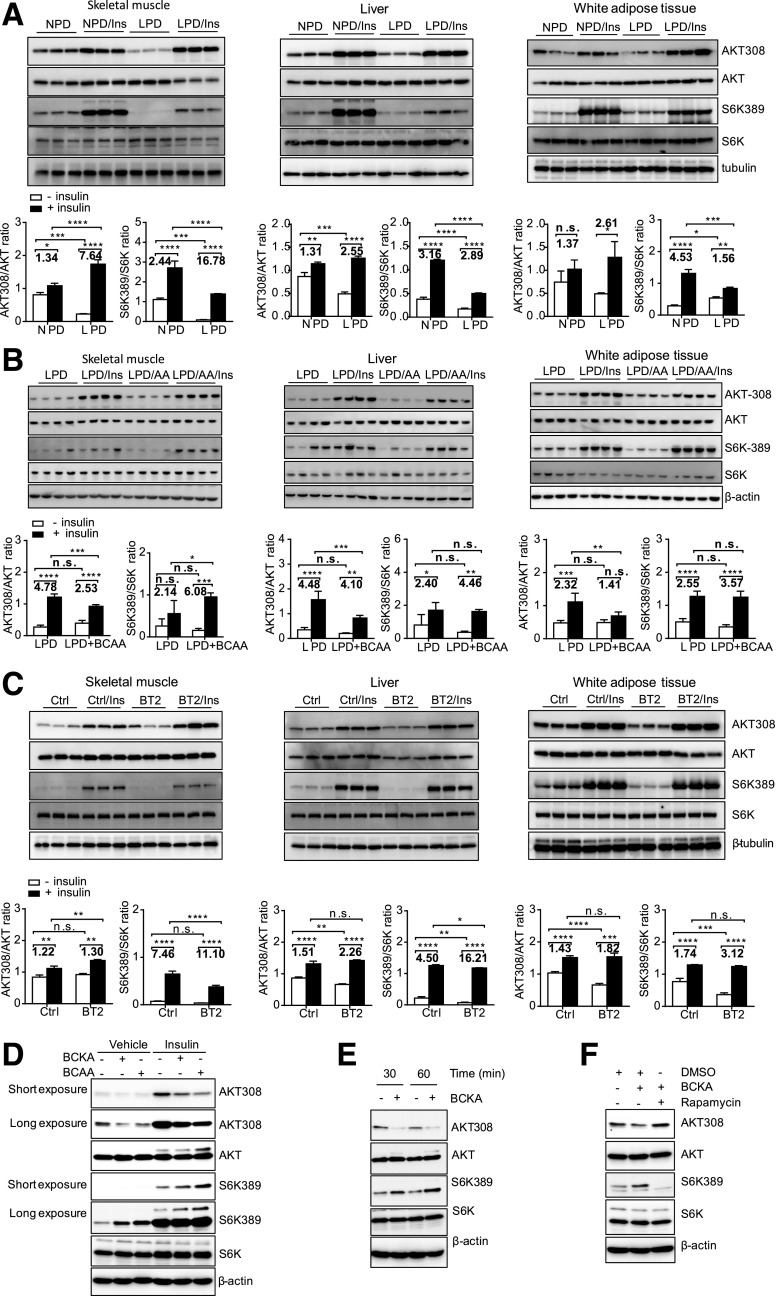
Figure 6.
BCAAs and BCKAs contribute to impaired insulin signaling in ob/ob mice. A–C: Representative immunoblots for specific proteins, created by using tissue lysates from skeletal muscle, liver, and white adipose tissue of mice without or with insulin (Ins) injection for 10 min following 6 h of food deprivation. ob/ob mice were fed an NPD (20% protein by weight) or an LPD (6% protein by weight) for 4 weeks beginning at 10 weeks of age (A). BCAA supplementation (LPD + BCAA or LPD/amino acids) in drinking water (3 mg/mL) was started after mice had consumed the LPD for 2 weeks and lasted 2 weeks (B). ob/ob mice were treated with the vehicle (Ctrl) or BT2 by oral gavage for 5 weeks (C). The graphs below the immunoblots in A–C present densitometric values of the bands. D–F: Representative immunoblots for specific proteins, created by using cell lysates. 3T3-L1 cells were treated with FBS- and BCAA-free DMEM for 1–2 h before BCAA (500 μmol/L), BCKA (500 μmol/L), or rapamycin (100 nmol/L) treatment for 1 h (D and F) or various times (E), followed by insulin treatment (10 nmol/L) for 1 h (D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.0001.