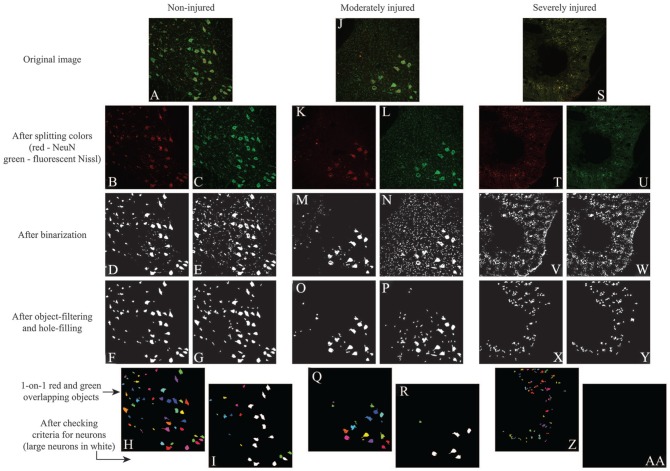
Figure 2.
Demonstration of the automated algorithm for counting neurons. In the (A) normal spinal cords, NeuN staining highlighted the (B) somas and (D) some non-soma-like objects, while FluoroNissl staining highlighted the (C) somas and (E) many non-soma-like objects. (F-H) Simple object-filtering was able to remove most of the non-soma-like objects in both stains. (I) The neuronal criteria helped to detect the objects that exhibited a clear nucleus and soma. In (J) moderately injured cord sites, both staining highlighted (K-N) the somas but also more non-soma-like objects comparing to normal. (O and P) Simple object filtering was able to remove most of the non-soma-like objects in both stains, but there were still a considerable number of them left. (Q) Checking double-stained objects helped to remove most of the remaining non-soma-like objects. (R) The neuronal criteria helped to remove the objects that did not exhibit a clear nucleus and soma. In (S) severely injured cord sites, both staining highlighted (T-W) many non-soma-like objects. Simple object-filtering was able to remove most of the non-soma-like objects in both stains, but there were still (X and Y) many non-soma-like objects left, and most of them were (Z) double-stained objects. The neuronal criteria helped to remove the remaining non-soma-like objects (aa).