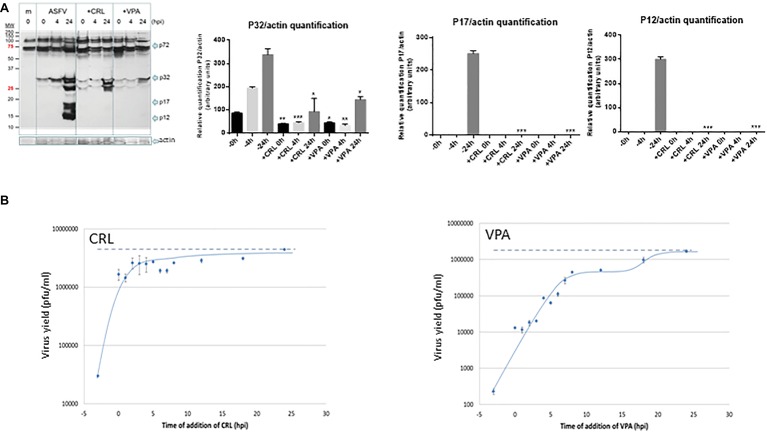
Figure 4.
(A) Effect of VPA and CRL on ASFV protein expression. Vero cells were preincubated or not with 20 mM VPA or 25 μM CRL and infected with ASFV Ba71V strain at a M.O.I of 2 pfu/cell. Non-adsorbed virus was washed away and the cultures maintained in the presence or absence of the AV to complete the virus cycle. Cell extracts obtained at different h.p.i. were subjected to western blot analysis to detect early (P32) or late (P17 and P12) ASFV-induced proteins in the presence or absence of the AV. ASFV-induced proteins are indicated by arrows. Molecular weight markers are shown (MW) in the left lane. Graphs show the relative quantification of bands corresponding to P32, P17, and P12 proteins versus actin expression control. Statistically significant differences between control and AV-treated cells are indicated by asterisks (Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (B) Effect of time of addition of VPA or CRL on their inhibitory activity. Vero cells were infected with ASFV Ba71V strain at a M.O.I. of 2 pfu/cell, and 20 mM VPA or 25 μM CRL was added at different times before or after infection, maintaining the presence of the AV up to the completion of virus cycle (24 h.p.i.) when total virus was titrated on Vero cell monolayers. Time 0 h.p.i. represents the end of virus adsorption (-2 to 0 h.p.i.). Dotted lines indicate the total virus production in the absence of inhibitor, corresponding to the value at 24 h.p.i.