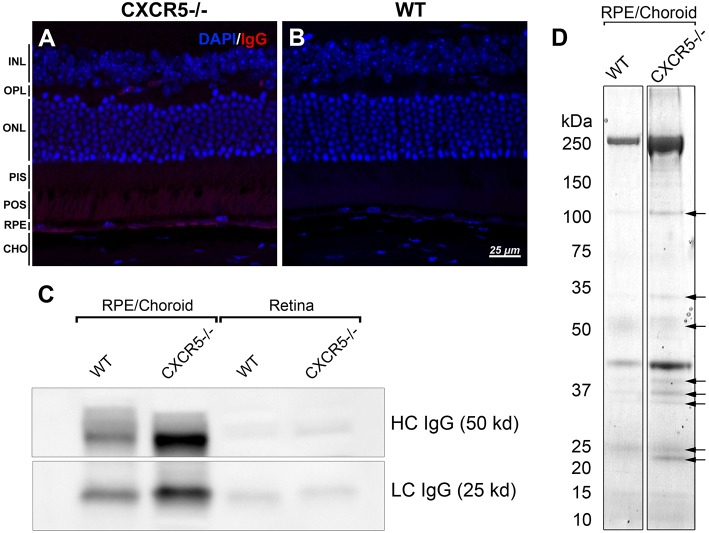
Figure 4.
Detection of endogenous IgG and antigen identification. (A) Fluorescent staining detected the presence of endogenous IgG of CXCR5−/−; with no signals detected in (B) WT control sections. (C) Increased heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) of IgG accumulation in RPE/choroidal complex of 24 m.o. CXCR5−/− mice when compared with age-matched WT controls. Sligh increase of HC IgG in the retina of CXCR5−/− mice. (D) Protein blots were incubated with purified serum from 17 m.o. WT and CXCR5−/− animals instead of a primary antibody for antigen identification. The identified bands (indicated by black arrows) were cut from the identical gel stained by Coomassie Blue and subjected to mass spectrometry analysis.