FIGURE 2.
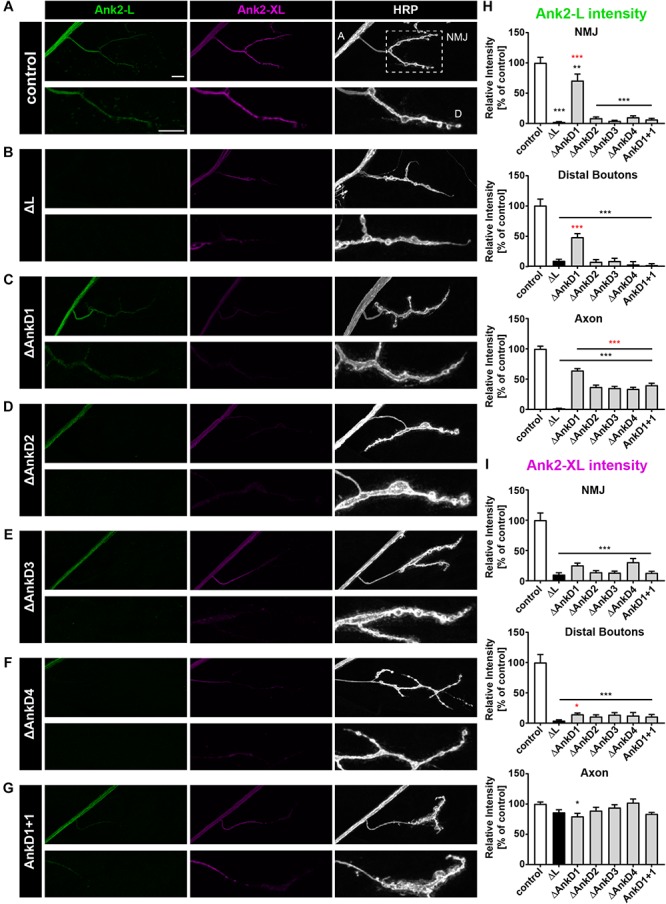
Analysis of ARD-dependent localization of Ank2-L and Ank2-XL in ank2ΔL mutants. (A–G) Analysis of Ank2-L (green) and Ank2-XL (magenta) localization at muscle 4 NMJs (HRP, white). (A) In control animals (P[ank2_wt]/+; ank2ΔL/ank2null) presence of the wild type P[acman] ank2 constructs completely restores NMJ localization of Ank2-L and Ank2-XL. Areas for quantification of intensities are indicated in the HRP channel (A, axon, D, distal bouton, NMJ). (B) In ank2ΔL/ank2null mutant animals Ank2-L is absent and levels of Ank2-XL are severely reduced at the NMJ but not in the axon. (C–F) Analysis of the four AnkD deletion mutants (P[ank2_ΔAnkDx]/+; ank2ΔL/ank2null) reveals severe perturbations of Ank2-L level at the NMJ. These effects are less severe for the AnkD1 mutation. All deletion mutations significantly reduce Ank2-XL distribution at the NMJ. (G) Analysis of the AnkD1+1 construct in which the second AnkD has been replaced by the first AnkD. Both Ank2-L and Ank2-XL distribution are perturbed comparable to the deletion of the second AnkD. (H) Quantification of Ank2-L level at the NMJ, within distal boutons and in the axon (n = 11–12 muscle 4 NMJs, three animals/genotype). (I) Quantification of Ank2-XL level at the NMJ, in distal boutons and in the axon (n = 11–12 muscle 4 NMJs, three animals/genotype). Scale bars in (A) apply to (A–G) and represent 10 μm. Error bars indicate SEM; *p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (ANOVA); black asterisks represent comparisons to controls; red asterisks represent comparisons to ank2ΔL mutants.
