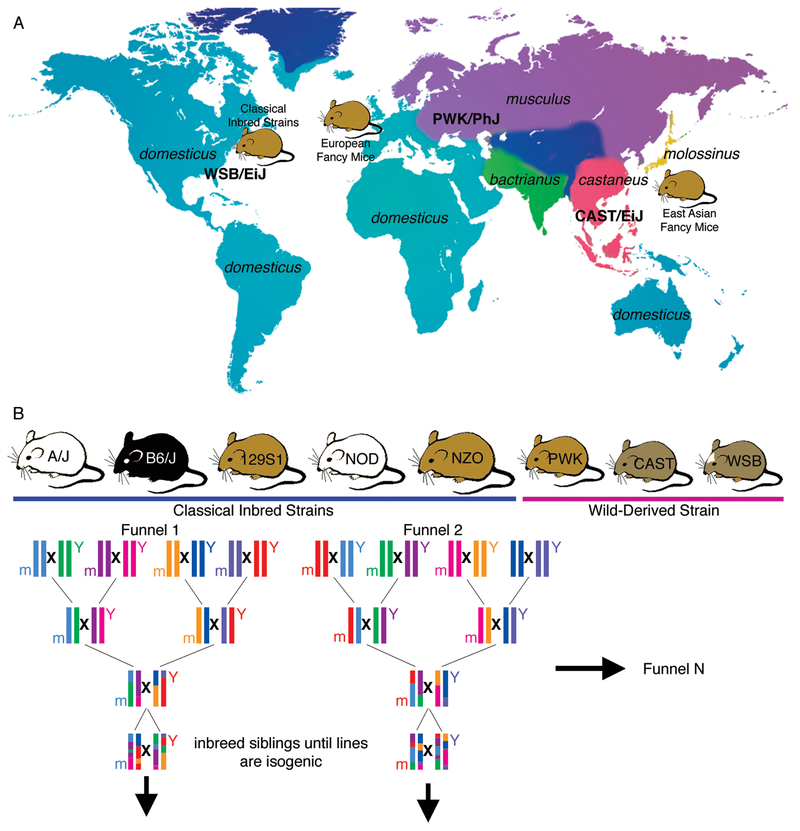
Figure 1:
(A) The distribution of Mus musculus subspecies and their contribution to modern day classical inbred strains. Classical inbred strains used in biomedical research were developed from European “fancy” mice that were descended from East Asian “fancy” mice. Classical inbred strains are mixtures of the domesticus, musculus, castaneus, and molossinus subspecies of Mus musculus. In addition, pure subspecies have been inbred to give rise to the “wild-derived” strains. WSB/EiJ is a M. m. domesticus strain originating in Maryland, USA. PWK/PhJ is a M. m. musculus strain originating near Prague, Czech Republic. CAST/EiJ is a M. m. castaneus strain originating in Thonburi, Thailand. (B) The design of the Collaborative Cross to maximize genetic diversity across a panel of recombinant inbred strains. Eight founder strains include 5 classical inbred strains and 3 wild-derived strains. By varying the position of each founder in the different breeding funnels, polymorphisms in the mitochondria (m) and the Y chromosome (Y) can be equally represented across the resulting lines.