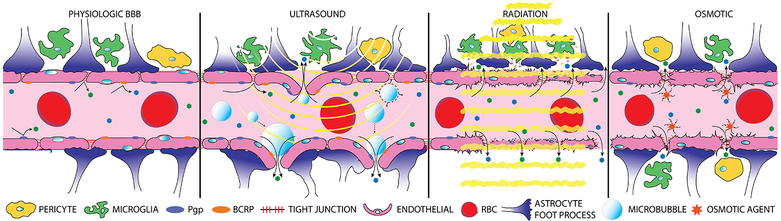
Figure 3, Key Figure. Blood-brain barrier disruption techniques.
Normal, undisrupted BBB with non-fenestrated endothelial cells sealed by tight junction proteins, further supported by astrocytic end-feet, pericytes, and microglia (a). Focused ultrasound (yellow curves) in combination with intravenously injected disrupts the BBB through cavitation and acoustic forces, ultimately leading to decreased molecular expression of tight junction proteins and an inflammatory response (b). Radiation therapy (yellow lines) disrupts the BBB through mechanisms of endothelial cell death and a neuro-inflammatory response from astrocytes and microglial cells (c). Hyperosmotic solutions are able to induce contraction and shrinkage of endothelial cells through a calcium dependent mechanism prompting widening of tight junctions (d).