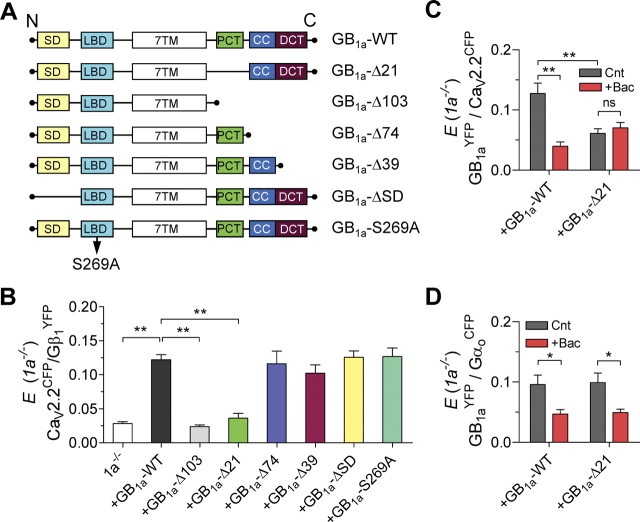
Figure 4.
Proximal C-terminal domain of the GB1a protein is essential for Gβγ/CaV2.2 channel association. A, Schematics show GB1a constructs used to examine the domain responsible for Gβγ/CaV2.2 association. SD, Two sushi domains; LBD, ligand-binding domain; 7TM, seven-transmembrane domain; PCT, proximal C-terminal domain; CC, coiled–coiled domain; DCT, distal C-terminal domain. B, Mean FRET for the indicated transfection conditions in 1a−/− neurons: GB1a-WT (n = 66, N = 11), GB1a-Δ103 (n = 44, N = 8, **p < 0.01), GB1a-Δ21 (n = 24, N = 6, **p < 0.0001), GB1a-Δ74 (n = 14, N = 4, p > 0.05), GB1a-Δ39 (n = 17, N = 4, p > 0.05), GB1a-ΔSD (n = 15, N = 4, p > 0.05), and GB1a-S269A (n = 14, N = 4, p > 0.05). One-way ANOVA analysis with post hoc Dunnett's multiple-comparison tests relative to 1a−/− boutons transfected with GB1a-WT indicated significance. C, Effect of 10 μm baclofen on the GB1aYFP/CaV2.2CFP FRET in 1a−/− boutons transfected with GB1a-WT (n = 7–20, N = 3–5, **p < 0.01) or GB1a-Δ21 (n = 23–24, N = 5–6, p > 0.05). D, Effect of 10 μm baclofen on the GB1aYFP/GαoCFP FRET in 1a−/− boutons transfected with GB1a-WT (n = 12–15, N = 3–4, *p < 0.05) or GB1a-Δ21 (n = 14–16, N = 3–5, *p < 0.05, paired t test). Error bars indicate SEM.