Figure 6.
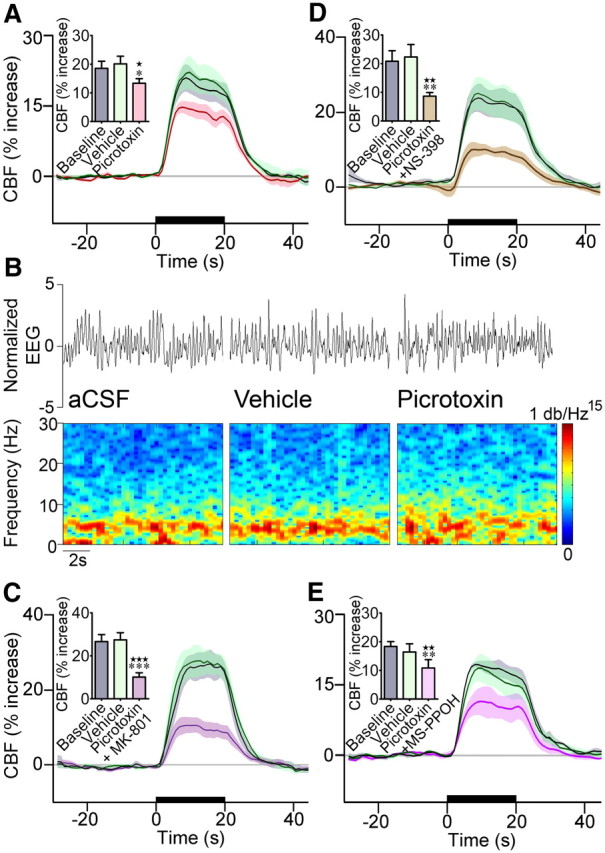
GABA-A receptor antagonism reduced the CBF response to whisker stimulation. A, One second average CBF responses to whisker stimulation measured at baseline, following vehicle or GABA-A receptor blockade after picrotoxin administration. Intracisternal injection of picrotoxin (A, n = 7) significantly reduced (∼31%) the evoked CBF response to whisker stimulation. B, Representative EEG trace (top) recorded from a single rat during baseline, vehicle, or picrotoxin superfusion through the cranial window. Power spectral densities (bottom) were obtained through a 1024-point short-time Fourier transform, using time windows of 1 s with 75% overlap. The frequency band from 0 to 30 Hz was normalized in amplitude from 0 to 1 and equalized with an exponential function with exponent 0.15, for better visualization. There was no change in the EEG between conditions. C, Combined administration of picrotoxin and MK-801 decreased the evoked CBF response (−61%, n = 8) significantly more than each compound applied individually (A, Fig. 4A,B). D, Combined administration of picrotoxin and NS-398 decreased the evoked CBF response (−52%, n = 7) more than each compound applied individually, but it did not reach significance (A, Fig. 4B). E, Similarly, combined GABA-A receptor blockade and inhibition of P450 epoxygenase with MS-PPOH decreased the evoked CBF response by ∼36%, which compared well with the inhibition induced by each compound individually (A, Fig. 4B). None of the vehicles had an effect on baseline or evoked CBF. The 20 s stimulation is indicated by the black line on the x-axis, and shaded areas denote SEM. Values are mean ± SEM. ★p < 0.05, ★★p < 0.01, ★★★p < 0.001 versus baseline. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by repeated-measures ANOVA.
