Figure 8.
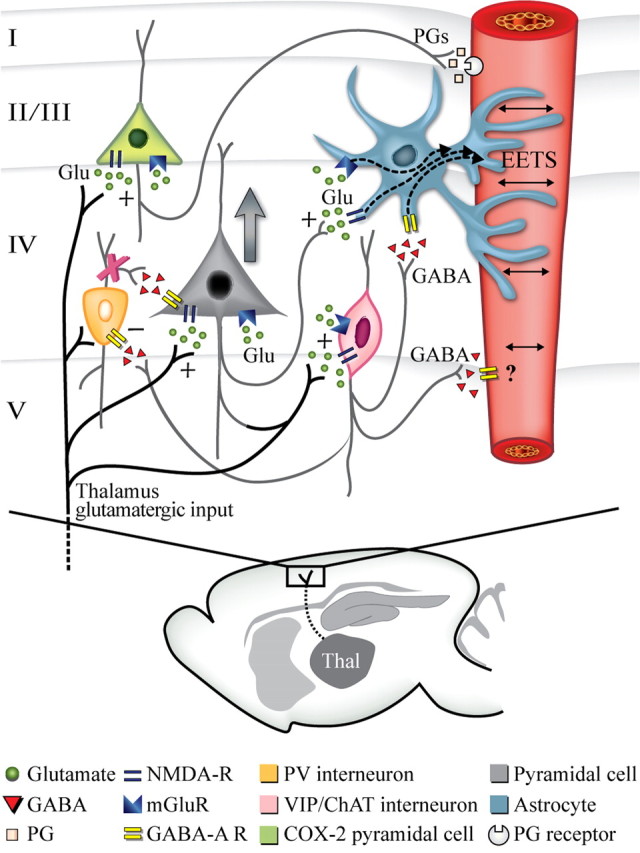
Schematic representation of the activated neuronal populations—identified with c-Fos—in the barrel cortex following whisker stimulation and how the different neuronal populations contribute to the evoked CBF response. Sensory thalamocortical glutamatergic afferents recruit pyramidal cells, including those that contain COX-2. These activated cells can then affect CBF either directly by the release of COX-2-derived dilatory prostaglandins (PGs) or indirectly by astrocytic release of EETs following activation of the P450 epoxygenase pathway, likely via mGluRs. Parallel activation of GABA interneurons that colocalize VIP and/or ChAT would modulate pyramidal cell excitation, in part, by silencing (−) PV and calbindin GABA interneurons, which would disinhibit pyramidal cells and enhance cortical activity (large gray arrow). GABA interneurons could also activate the EET pathway in astrocytes through GABA-A-mediated increase in calcium transients. The × on PV interneurons reflects the blockade of their inhibitory drive on pyramidal cells exerted by the recruited VIP/ChAT interneurons, which results in disinhibition of pyramidal cells.
