Figure 2.
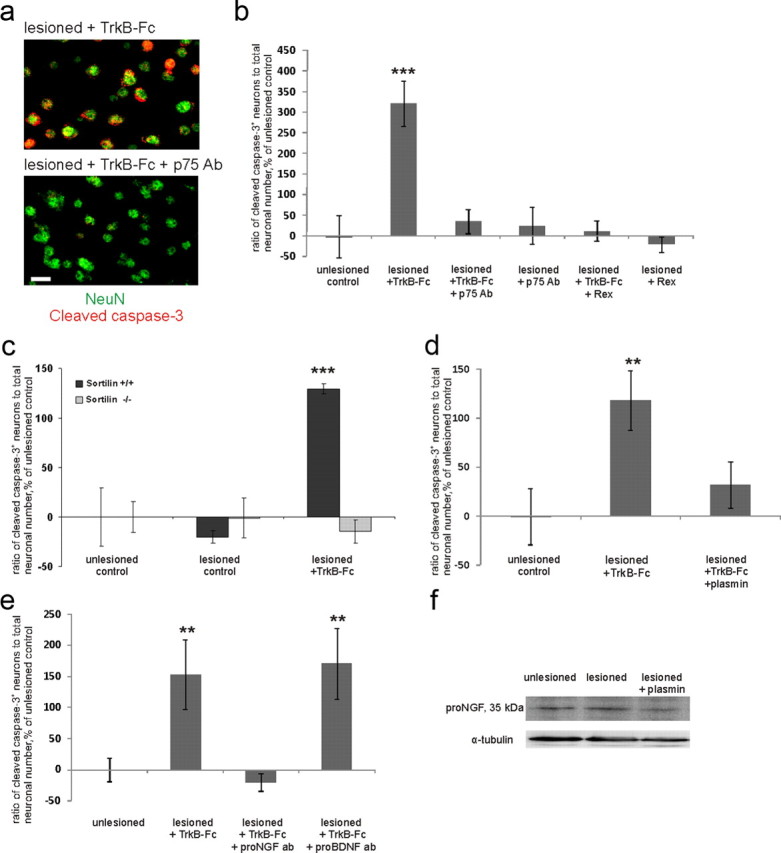
Posttraumatic emergence of the requirement for BDNF is caused by p75NTR. a, Images of axotomized TrkB-Fc-treated neurons with and without p75NTR-blocking antibodies obtained similarly to those in Figure 1b. Scale bar, 10 μm. b, Ratio of cleaved caspase-3-positive (=apoptotic) neuronal number to total neuronal number obtained by blind stereological counting, percentage of unlesioned control ratio value. Treatment with two different function-blocking antibodies directed against the extracellular domain of p75NTR [p75 Ab; AB1554; Millipore; and Rex (Weskamp and Reichardt, 1991)] abolished the increase in the number of apoptotic neurons promoted by TrkB-Fc. n = 46 slices/4750neurons; ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post hoc analyses. c, TrkB-Fc treatment did not induce caspase activation in sortilin knock-out mice. Quantification was performed as in b; n = 48 slices/4600 neurons; ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post hoc analyses. d, Treatment with plasmin abolished the TrkB-Fc-induced increase in the number of apoptotic neurons. Quantification was performed as in b; n = 33 slices/3350 neurons; **p = 0.017, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post hoc analyses. e, Treatment with antibodies toward proNGF completely prevented TrkB-Fc-induced death induction, whereas antibodies toward proBDNF had no effect. n = 41 slices/3420 neurons; **p = 0.05, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post hoc analyses. f, Western blot analyses with the antibody to proNGF. proNGF expression was upregulated by lesion and diminished by plasmin. n = 3 experiments/36 slices; **p = 0.041, one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's post hoc analyses. For full image of the representative blot, see Figure 3a. Error bars indicate SEM.
