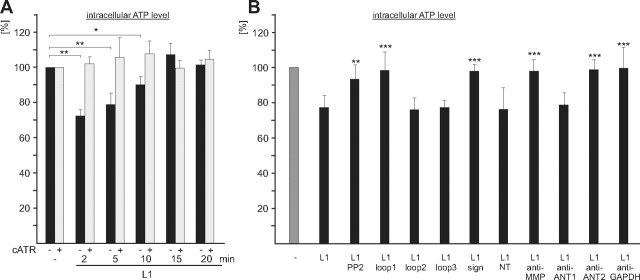
Figure 8.
Stimulation of L1 functions at the cell surface leads to a transient reduction of intracellular ATP levels. A, B, Live cerebellar neurons were incubated without or with L1-Fc for different time periods in the absence (−) or presence (+) of carboxyatractyloside (cATR) (A), or were incubated for 3 min without (−) or with L1-Fc (L1) in the presence of PP2 or ANT-derived peptides containing loop 1, loop 2, loop 3, the signature motif (sign), or N-terminal amino acids 1–28 of ANT1, ANT1- or ANT2-specific antibodies (anti-ANT1; anti-ANT2), or antibodies against MMP14 (anti-MMP) or GAPDH (anti-GAPDH) (B). ATP levels in cell lysates are shown relative to the level obtained in the absence of L1-Fc, which was set to 100%. Mean values ± SD from triplets of three independent experiments are shown, and values that are significantly different from the values obtained upon treatment of neurons with L1-Fc without additives are indicated by asterisks: *p < 0.001; **p < 0.0001; ***p < 0.00001 (Student's t test).