Figure 1.
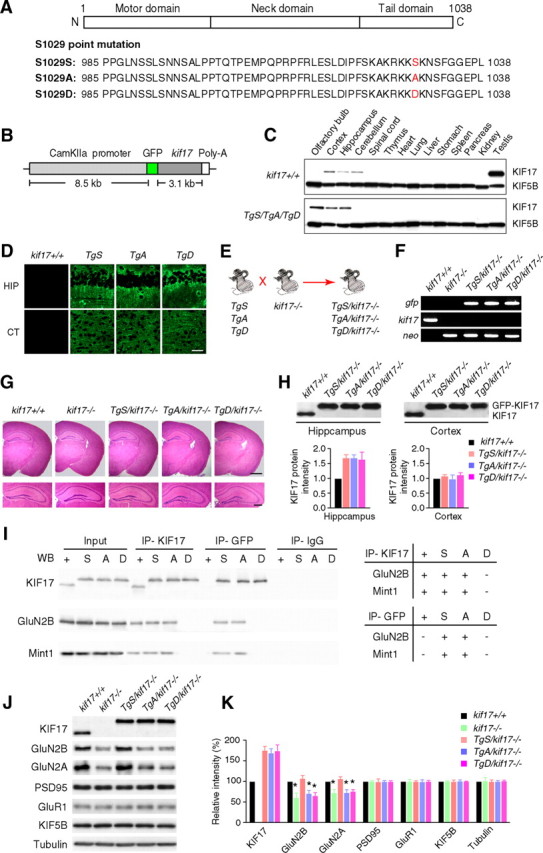
Generation and biochemical characterization of KIF17 transgenic mouse lines. A, Point mutation of the C-terminal domain KIF17 at Ser1029. The C-terminal domain of KIF17 is critical for cargo binding. Ser1029 is phosphorylated by CaMKII to regulate the KIF17–Mint1 interaction. S1029S: wild-type KIF17. S1029A: substitution of Ser1029 by Ala, which mimics the unphosphorylated state. S1029D: substitution of Ser1029 by Asp, which mimics the phosphorylated state. B, The construct for generation of KIF17 transgenic mice. KIF17 expression was restricted to the postnatal forebrain because of the use of CaMKIIα promoter. C, Expression of KIF17 in various tissues. KIF5B was used as a control. In transgenic mice, GFP-KIF17 was restricted to the postnatal forebrain (olfactory bulb, hippocampus, and cortex) by using the CaMKIIα promoter. D, Immunohistochemistry to examine KIF17 localization in forebrain regions: hippocampal CA1 (HIP) and cortex (CT) subregions. Scale bar, 100 μm. E, Schematic illustration of the procedure used to generate Tg+/kif17−/− mice. KIF17 transgenic mice (TgS, TgA, and TgD) were bred with kif17−/− mice to generate three new transgenic mouse lines with disrupted endogenous kif17 gene (TgS/kif17−/−, TgA/kif17−/−, and TgD/kif17−/−). F, PCR screening using primers for gfp, neo, and endogenous kif17. G, Paraffin sections of the mouse brain stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bars, 500 μm (top right) and 200 μm (bottom right). H, Western blot analysis and quantification of GFP-KIF17 in the hippocampi and cortices of Tg+/kif17−/− mice. The lower bands indicate endogenous KIF17, and the upper bands indicate GFP-KIF17 fusion proteins. I, Immunoprecipitation of mouse hippocampal extracts using anti-KIF17 and anti-GFP antibodies; anti-IgG antibody was used as a negative control. J, K, The levels of KIF17, GluN2B and other associated proteins in the hippocampus of transgenic mice. Data from three independent experiments are expressed as mean ± SEM (*p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA and post hoc comparison test).
