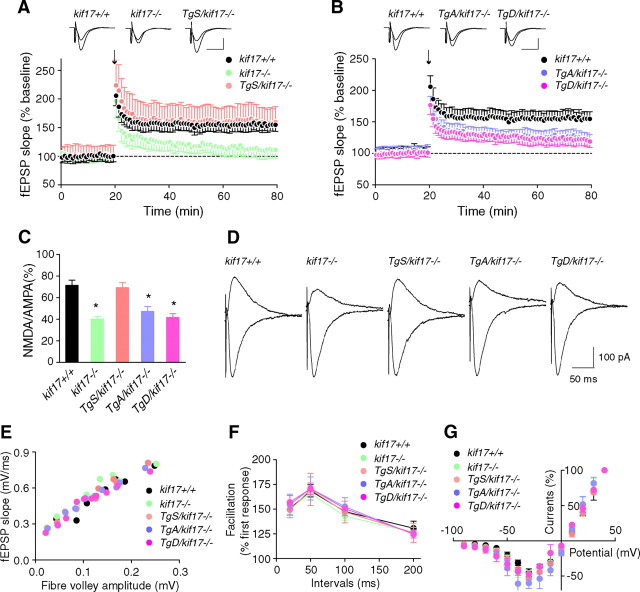
Figure 3.
Synaptic NMDA receptor-mediated LTP and EPSCs. A, B, LTP induced by a single train of tetanus (100 Hz for 1 s, arrow) in hippocampal CA1 neurons of kif17+/+, kif17−/−, and Tg+/kif17−/− mice. Sample traces show typical fEPSPs recorded 5 min before and 60 min after LTP induction. Expression of LTP was attenuated in kif17−/−, TgA/kif17−/− and TgD/kif17−/− slices. C, D, AMPA- and NMDA-mediated EPSCs recorded in CA1 pyramidal neurons of kif17+/+, kif17−/−, and Tg+/kif17−/− mice. NMDA/AMPA ratios in neurons from kif17−/−, TgA/kif17−/− and TgD/kif17−/− mice were decreased, consistent with a decrease in NMDA-mediated currents (mean ± SEM, *p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA and post hoc test). NMDA/AMPA ratios in neurons of kif17+/+ and TgS/kif17−/− mice were not different. E, Input–output curves plotting the fEPSP slopes against their corresponding presynaptic fiber volley amplitudes. Each symbol represents a set of experiments from a single slice. F, Paired-pulse facilitation of fEPSPs was measured using pairs of presynaptic fiber stimulation pulses separated by 20, 50, 100, and 200 ms. For each group, the mean ± SEM is indicated. G, Current–voltage relationship of NMDA receptor channel currents recorded in hippocampal slices. Current amplitudes were normalized to the values at +40 mV EPSC. Values are mean ± SEM.