Figure 5.
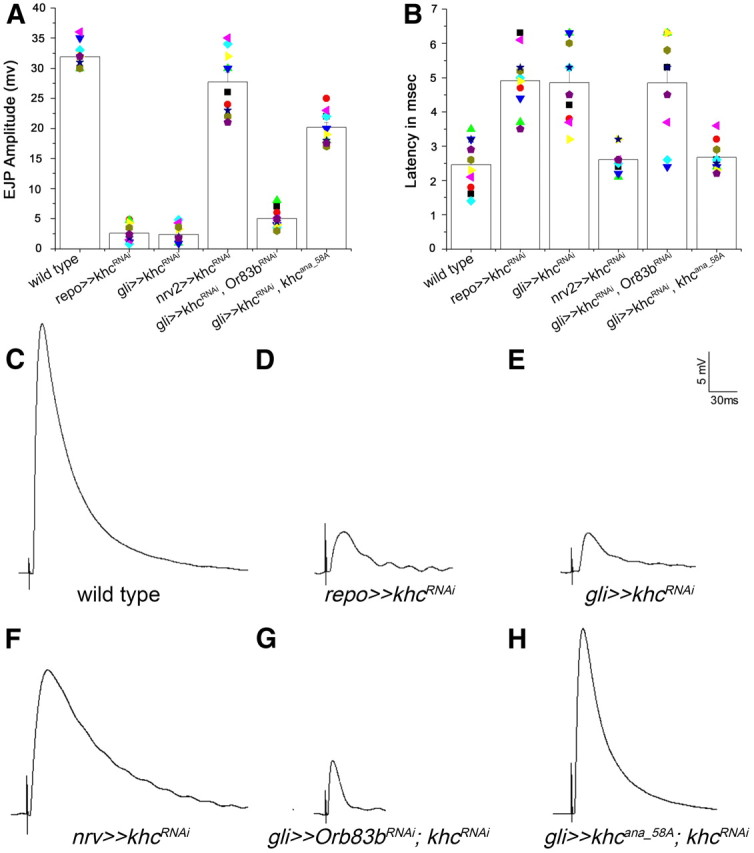
Glial khc knockdown affects neuronal activity. A, Comparison of evoked EJPs upon silencing khc in glial cells. Amplitudes of evoked EJPs after activating the A6 motor neuron at muscle 6 in response to a 0.3 ms voltage stimulus were determined. B, The latency of the muscle response is depicted. Glial reduction of khc results in delayed responses. C, Example of a wild-type response. D, E, Responses of silencing khc using dsRNA expression in all glial cells (repo≫khcRNAi) and specifically in the subperineurial glial layer (gli≫khcRNAi) were similar in amplitudes and duration to spontaneous EJPs. Control larvae showed much higher amplitudes (p < 0.001). Minis or spontaneous EJP responses were normal and similar in all the genotypes tested. F, No significance difference was observed in nrv2Gal4, UASkhdsRNA animals with control responses (p > 0.05). G, H, Coexpression of khcana_58A and khcdsRNA but not of Or83bdsRNA and khcdsRNA rescued the neuronal responses (p < 0.01). Pooled data are presented as means ± SE.
