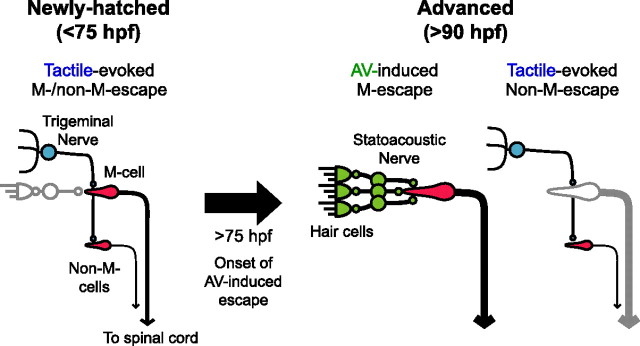
Figure 7.
Schematic drawings of fast escape circuit before and after acquisition of AV-induced escape, reflecting developmental events described in Discussion. Before 75 hpf, head-tactile input through the trigeminal nerve initiates both M- and non-M-escape. After 75 hpf, developing AV input becomes effective to fire the M-cell and AV-induced escape is acquired. In the meantime, trigeminal input becomes ineffective to fire the M-cell after 90 hpf, although it still triggers non-M-escape. In both stages, the M-cell is necessary to initiate escape with minimal latency. Non-active or ineffective pathways are colored in gray. Thicker descending axons from the M-cells or non-M-cells represent shorter conduction times.