Figure 4.
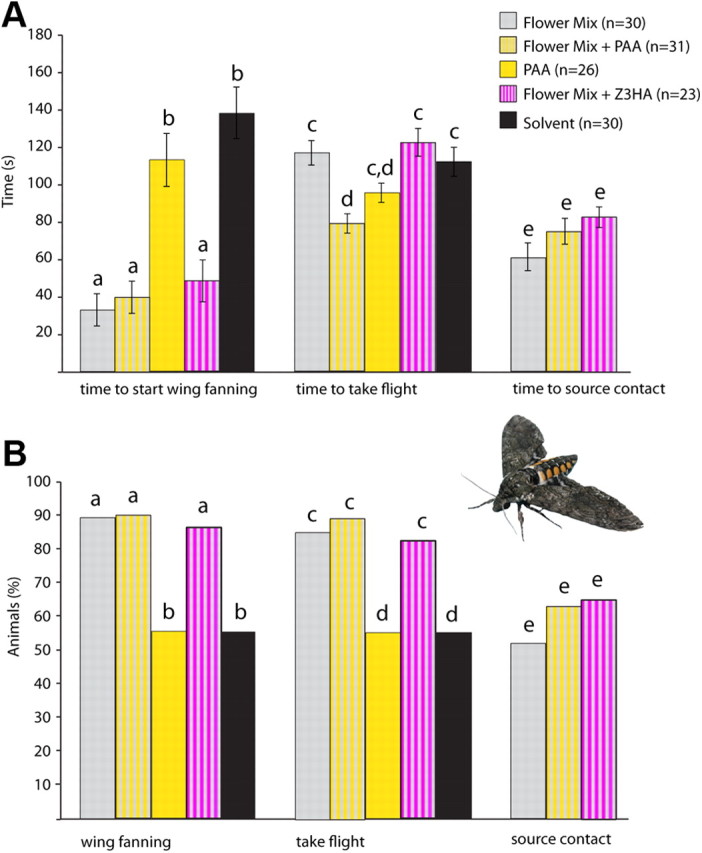
Behavioral correlates of AL network processing. The behavioral activity of PAA and Z3HA was assessed in a wind tunnel assay. We examined upwind flight and source contact behavior to a behaviorally attractive synthetic 3-component mixture (Flower Mix, determined by Riffell et al., 2009), with and without the addition of 1% PAA or Z3HA to the mixture (Flower Mix, n = 30, gray bars; Flower Mix + PAA, n = 31, gray/yellow striped bars; PAA, n = 26, yellow bars; Flower Mix + Z3HA, n = 23, gray/magenta striped bars; Solvent (mineral oil) n = 30, black bars). A, Average time elapsed during olfactory behavior. Moths took flight significantly faster when PAA was added to the synthetic Flower Mix (p = 0.01, t test), but not when PAA was presented alone. Substitution of another component (Z3HA; also compare Fig. 3) neither changed activity nor enhanced source contact in moths. B, Percentages of moths displaying each behavioral characteristic tested. Nearly all (at least 85% total) animals that started wing fanning also took flight. Note that the number of source contacts (∼60%) was not affected by adding PAA or Z3HA. In contrast, PAA or the mineral oil control alone elicited wing fanning and flight in only 50% of animals tested with no source contact or oriented flight observed.
