Figure 4.
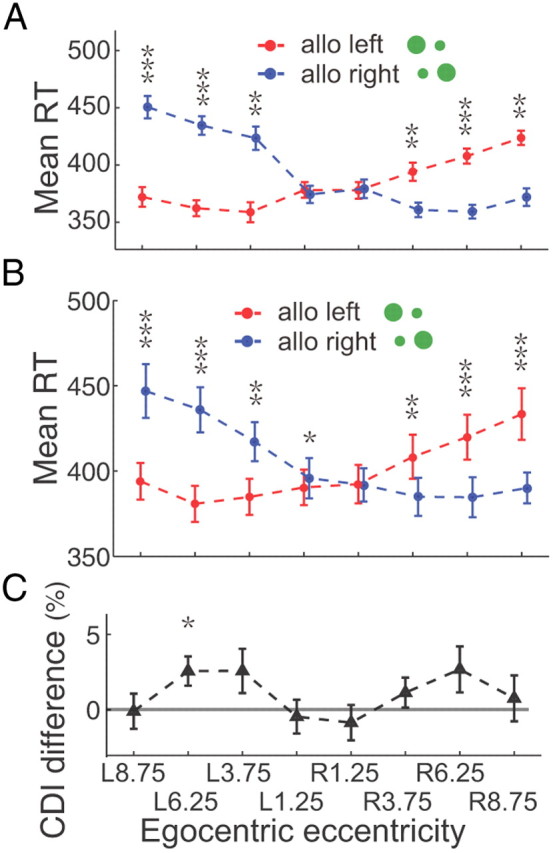
RT in the Crossed-hand task. A, The example subject's averaged RTs with SEM are plotted in red (allocentric left) and blue (allocentric right) correlated with target's egocentric locations. RTs are significantly smaller in compatible condition than in incompatible condition in 6 peripheral egocentric locations (the maximum p = 0.0044, Wilcoxon test). B, The average RTs of 9 subjects. The population data show significantly smaller RT in the compatible condition than that in incompatible condition in 7 of 8 egocentric locations (the maximum p = 0.0013 for egocentric left and 0.0406 for egocentric right, two-tailed t test). C, CDI difference between crossed-hand task and uncrossed-hand (main) task. The CDI differences are close to 0 in 7 of 8 egocentric locations (the minimum p = 0.1347, two-tailed t test).
