Fig. 6.
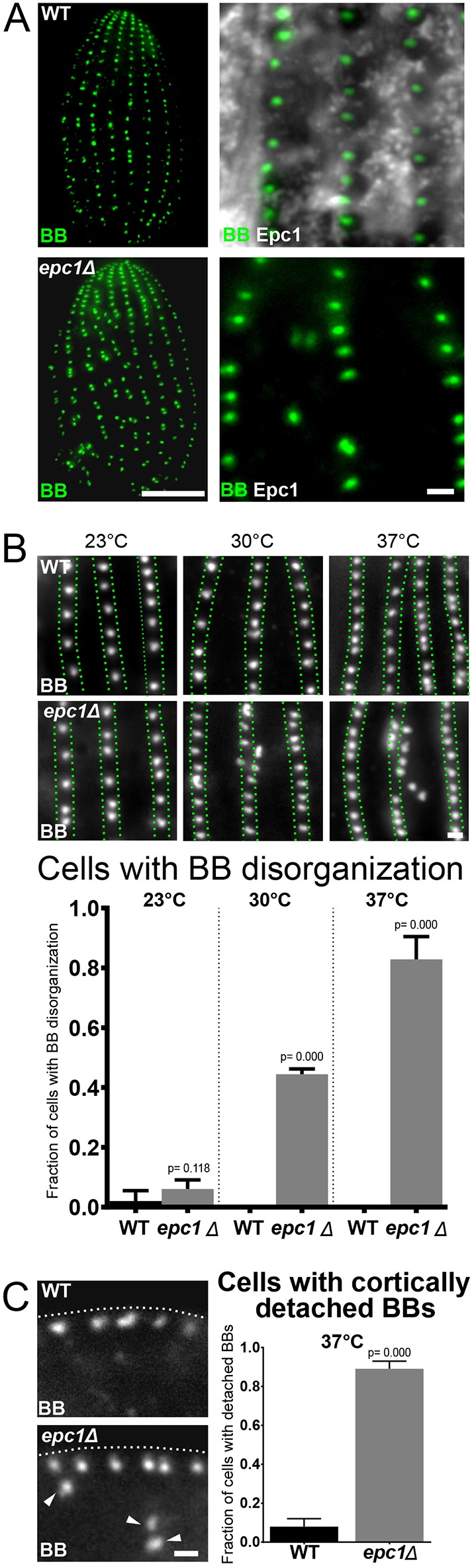
Cortical epiplasm is required for BB organization and cortical attachment. (A) Images showing the dorsal side (side without oral apparatus) of WT and epc1Δ cells labeled for BBs (Centrin, green). Scale bar: 10 µm. Magnified images from of WT and epc1Δ cells showing BBs (Centrin, green) and epiplasm (Epc1, grayscale). Scale bar: 1 µm. epc1Δ cells have disorganized BBs. (B) Top panels: Images of WT and epc1Δ cells grown at 23°C, 30°C and 37°C for 24 h, labeled for BBs (Centrin, grayscale). Scale bar: 1 µm. Green dotted lines denote boundaries of BB rows. Bottom panels: Elevated temperature increases BB disorganization in epc1Δ cells (WT 23°C: n=99 cells, epc1Δ 23°C: n=99 cells, WT 30°C: n=99 cells, epc1Δ 30°C: n=99 cells, WT 37°C: n=99 cells, epc1Δ 37°C: n=99 cells). (C) Left panel: Images showing a longitudinal section through BBs (Centrin, grayscale) at the cell cortex in WT and epc1Δ cells. Arrowheads denote BBs that are detached from the cell cortex. Dotted white line denotes the location of cell cortex as determined by the cellular fluorescence background. Scale bar: 1 µm. Right panel: Graph shows quantification of the proportion of cells with detached BBs. At 37°C, epc1Δ cells have more cortically detached BBs than WT cells (WT 37°C: n=63 cells, epc1Δ 37°C: n=64 cells).
