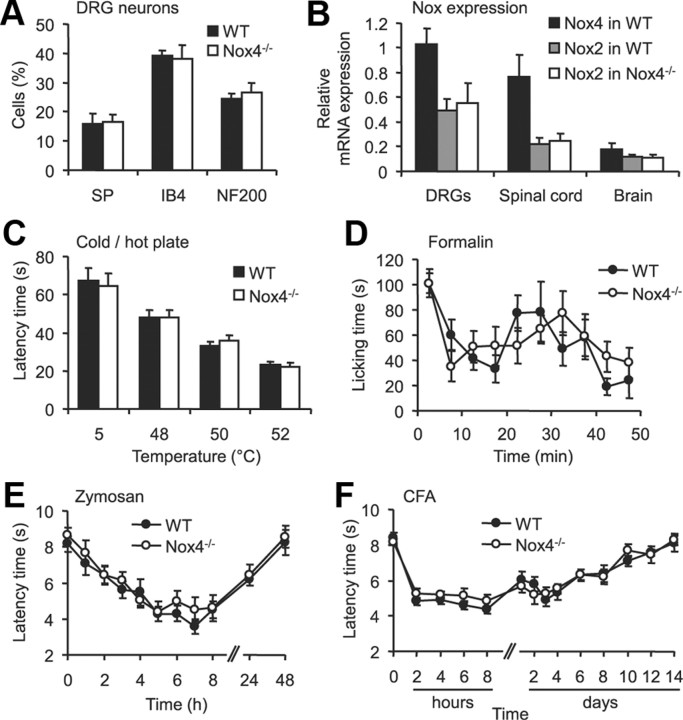
Figure 2.
Basal characteristics, acute pain behavior, and inflammatory pain behavior are not impaired in Nox4−/− mice. A, Percentages of DRG neurons binding IB4 or immunoreactive for substance P (SP) or NF200 were similar in WT and Nox4−/− mice (3340 cells counted, n = 3–4 mice per genotype). B, Expression of Nox mRNA in DRGs, spinal cord and brain of WT and Nox4−/− mice assessed by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Nox4 mRNA was only detected in tissues from WT mice, whereas Nox2 mRNA levels were similar in tissues from WT and Nox4−/− mice. Nox1 or Nox3 mRNA were not reliably detected (Ct values > 35) in both genotypes (n = 3–4). C, Cold-plate and hot-plate tests. The latency of Nox4−/− mice to exhibit nocifensive behaviors was similar to that of WT littermates at cold (5°C) and hot (48–52°C) temperatures (n = 12). D, Formalin test. Both genotypes showed a similar biphasic response to 5% Formalin injected into a hindpaw (n = 8). E, F, Paw-withdrawal latency times after mechanical stimulation after injection of zymosan (E) or CFA (F) into a hindpaw. Mechanical hypersensitivity did not differ between genotypes at all times tested (n = 7–9). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.