Figure 8.
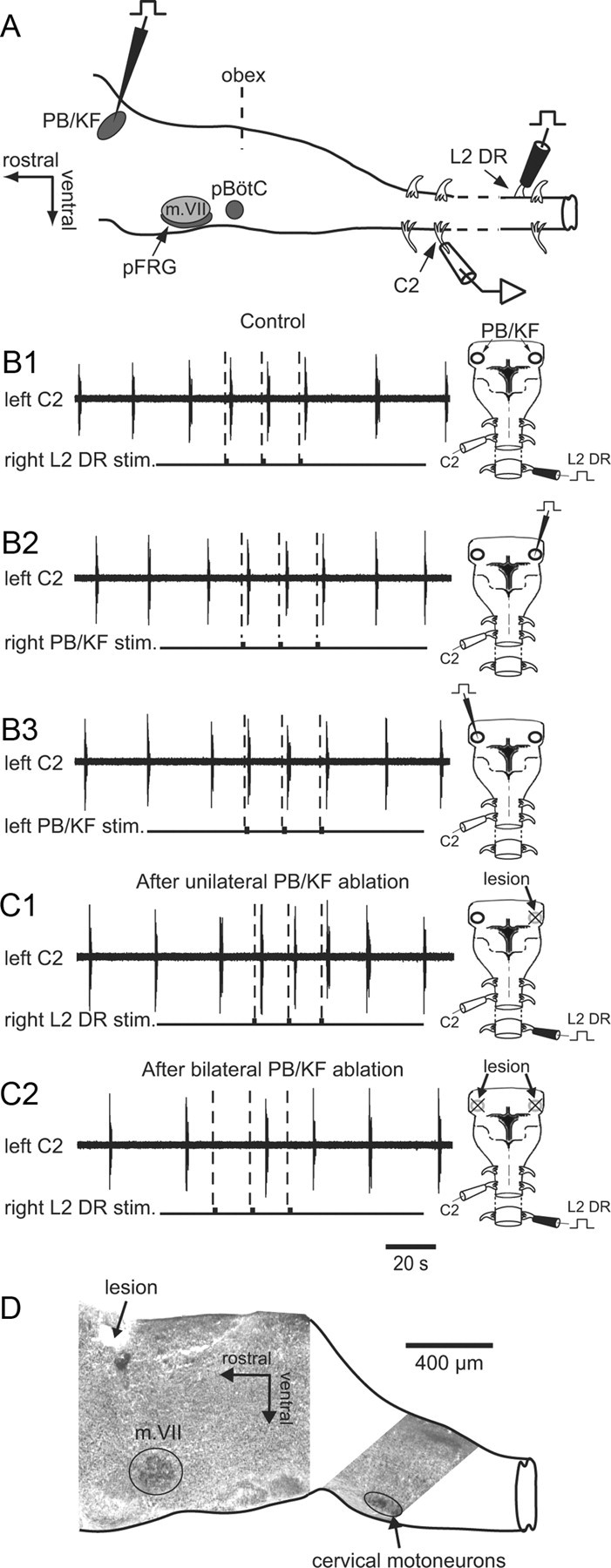
Spinal afferent-entrained respiratory bursting involves the PB/KF complex as a pontine relay. A, Schematic representation of brainstem structures (lateral view) and experimental procedures. B, Right, Dorsal view diagrams of the brainstem/spinal cord preparation showing stimulating and recording electrode positions. Left, C2 ventral root recordings of inspiratory bursting during cyclic electrical stimulation of the contralateral L2 DR (B1) or during direct stimulation of the contralateral (right PB/KF stim., B2) or ipsilateral (left PB/KF stim., B3) PB/KF. Respiratory rhythm entrainment occurred with all three stimulus paradigms. C, Persistence (C1) or suppression (C2) of respiratory entrainment following unilateral (C1) or bilateral (C2) electrolytic lesions to the PB/KF nuclei, respectively. D, Parasagittal AChE-stained section as a histological control. The locality of the electrolytic lesion near the dorsal brainstem surface corresponded to the location of the PB/KF complex. m. VII, facial motor nucleus; pBötC, pre-Bötzinger complex; pFRG, parafacial respiratory group.
