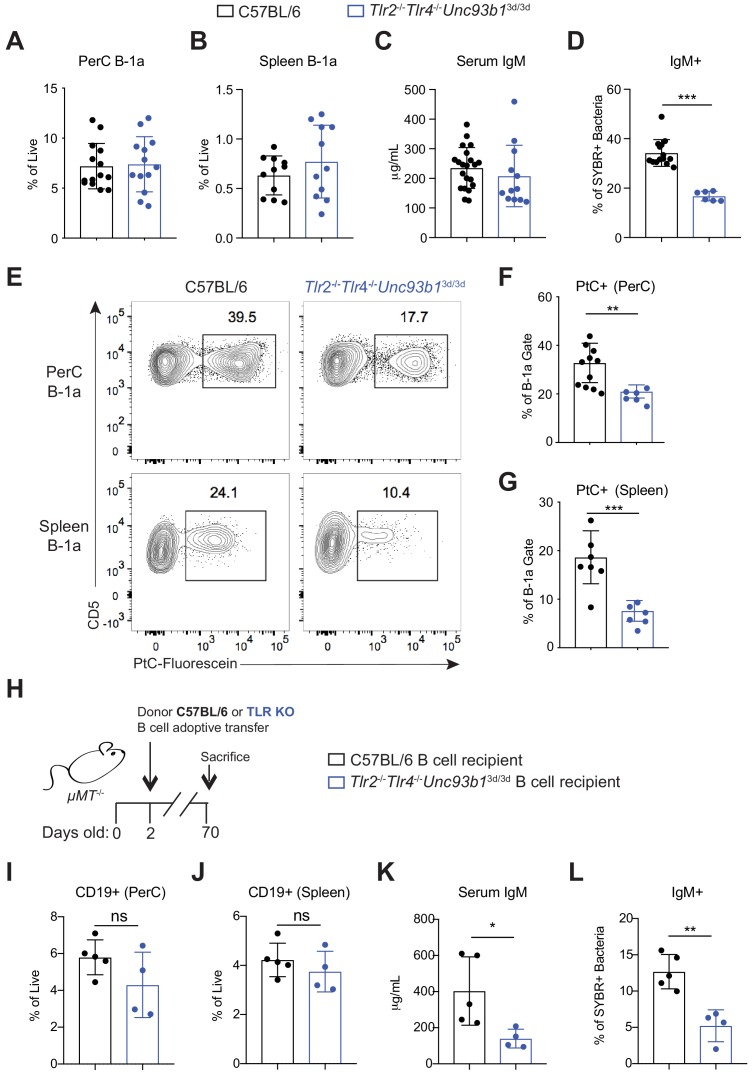
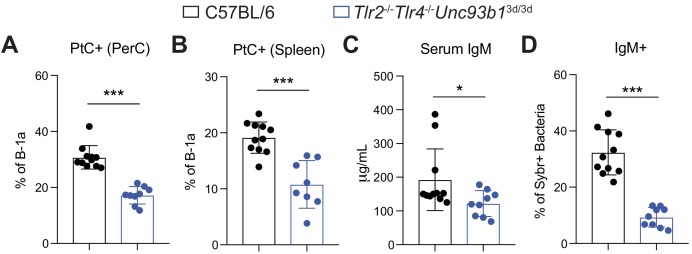
Figure 4. Loss of Toll-like receptor signaling results in reduced B-1a responses to both phosphatidylcholine and the microbiota.
(A) Frequency of live B-1a cells in 7 wk old WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) mice in the peritoneal cavity (PerC) and (B) spleen, as measured by flow cytometry. B-1a cells defined as CD19+CD23–CD43+CD5+. (C) Serum IgM titers in 7 wk old WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) mice, as measured by ELISA. (D) Percentage of SYBR+μMT-/- fecal bacteria bound by serum IgM from WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) mice, as measured by flow cytometry. (E) Representative flow cytometry plot and quantification (F-G) of percentage of B-1a cells in the (F) peritoneal cavity (PerC) and (G) spleen bound by fluorescein-labeled phosphatidylcholine liposomes in 7 wk old WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) mice. (H) Schematic showing adoptive transfer of CD19+ pooled bone marrow and spleen cells (B cells) from either C57BL/6 (WT) (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) into B cell deficient μMT-/- recipeint mice at 2 days of age and sacrificed at 10 weeks of age. (I-J) Frequency of live B-1a cells in 7 wk old WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) B cell recipient mice in the (J) peritoneal cavity (PerC) and (J) spleen, as measured by flow cytometry. (K) Serum IgM titers in 7 wk old WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) B cell recipient mice, as measured by ELISA. (L) Percentage of SYBR+ fecal bacteria bound by serum IgM from WT (black) or Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d (blue) B cell recipient mice, as measured by flow cytometry. Error bars indicate the mean (± SEM). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test). Each data point represents an individual mouse. Data are pooled from at least three independent experiments (A-G; I-L).