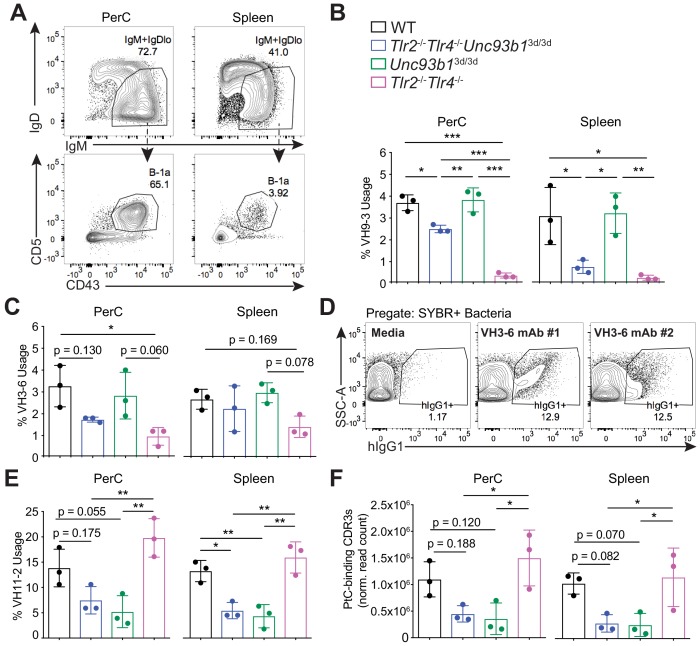
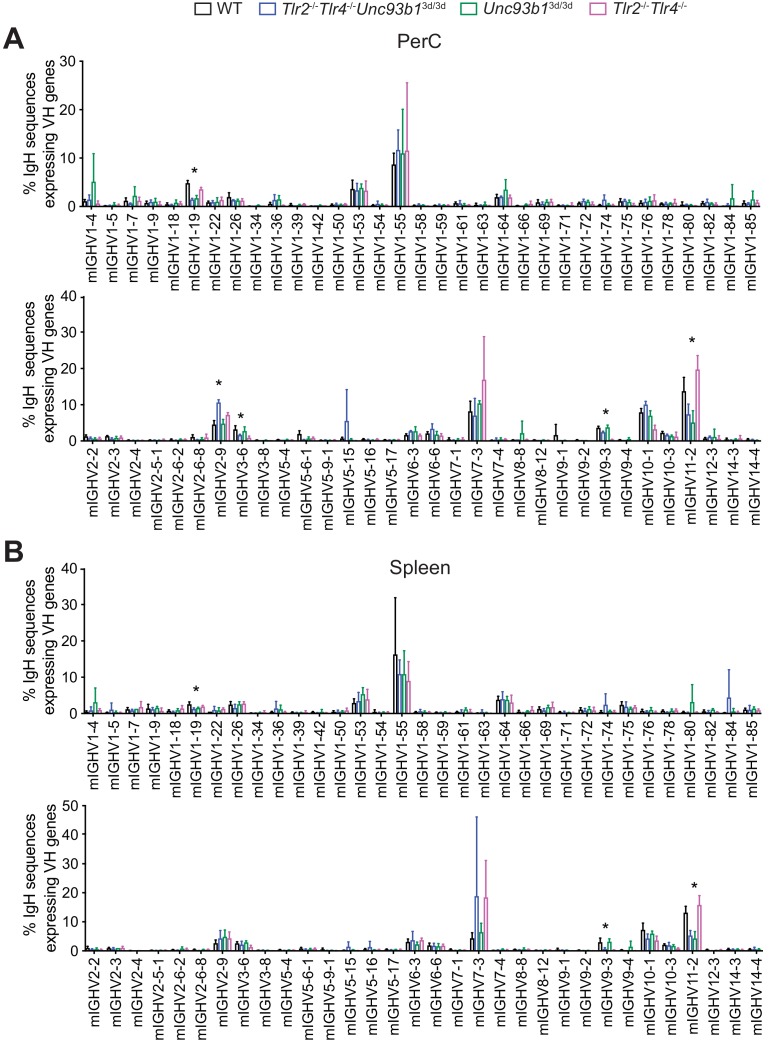
Figure 6. B-1a immunoglobulin repertoire analysis reveals unique regulation of a subset of heavy chain genes by distinct subsets of TLRs.
(A) Representative flow cytometry gating strategy for sorting IgM+IgDloCD43+CD5+B-1a cells (pregated as CD19+/DAPI–) in the peritoneal cavity (PerC) (left) and spleen (right). Prior to sorting, splenocytes were depleted of CD3+CD4+CD8+F4/80+NK1.1+GR-1+ cells using biotinylated antibodies and streptavidin magnetic beads. (B-C) The percentage of heavy chain CDR3 nucleotide sequencing reads expressing the germline (B) VH9-3 allele or the (C) VH3-6 allele in peritoneal cavity (PerC) (left) and spleen (right) B-1a samples (% usage). (D) Percentage of pre-gated SYBR+ fecal bacteria bound by two individual recombinant hIgG1 monoclonal antibodies (#1 and #2) expressing the germline VH3-6 allele generated from splenic B-1a cells from 6 wk old mice, described in Figure 2C, as measured by flow cytometry. (E) The percentage of heavy chain CDR3 nucleotide sequencing reads expressing the germline VH11-2 allele in peritoneal cavity (PerC) (left) and spleen (right) B-1a samples (% usage). (F) The combined normalized read counts of PtC-binding CDR3 peptide sequences (MRYSNYWYFDV, MRYGSSYWYFDV, and MRYGNYWYFDV) in peritoneal cavity (PerC) (left) and spleen (right) B-1a samples. Black circles represent WT mice, blue circles represent Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/-Unc93b13d/3d mice, green circles represent Unc93b13d/3d mice, and pink circles represent Tlr2-/-Tlr4-/- mice (B, C, E, F). CDR3 frequencies were artificially scaled to 10 million reads to account for differences in read depth among samples (F). Error bars indicate the mean (± SEM). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (One-way ANOVA). Each data point represents an individual mouse (B, C, E, F). Data representative of 3 independent experiments (D). There are three source files associated with this figure.