Fig. 5. Brain surface characters in tarsier and anthropoids mapped onto phylogeny emphasizing platyrrhine relationships.
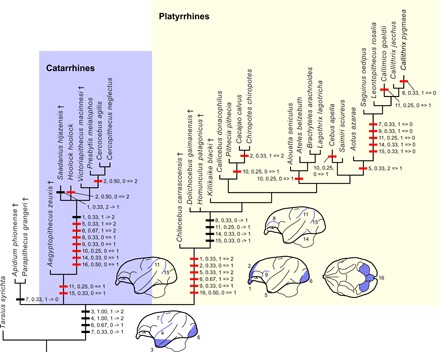
Apomorphic characters are mapped on the phylogenetic tree inferred from Bayesian tip dating based on the total evidence analyses of phenomic and molecular data (fig. S1). Parsimony is used for mapping the characters. Fossil taxa are indicated by † (dagger symbol). Taxa lacking preserved brain surface features are omitted. Thick horizontal bars represent a brain surface character, followed by the character’s number (see below), its consistency index, and the state change. Red bars indicate unambiguously optimized. Character codes: (1), relative size of the olfactory bulb: 0, very large; 1, large; and 2, small; (2), overlap of the olfactory bulb by the frontal lobe: 0, less than half; 1, half; and 2, full; (3), expansion of the temporal lobe: 0, absent; 1, present and temporal lobe projects slightly downward; and 2, present and temporal lobe projects downward substantially; (4), Sylvian sulcus: 0, absent; 1, shallow and short; and 2, deep and long; (5), exposure of the piriform lobe in lateral view: 0, very large; 1, small; and 2, absent or very small; (6), degree to which occipital pole overlaps cerebellum: 0, none; 1, partial; and 2, fully; (7), central sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (8), sulcus rectus: 0, absent and 1, present; (9), arcuate sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (10), superior precentral sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (11), intraparietal sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (12), caudal part of the sulcus rectus approaches the intraparietal sulcus: 0, yes and 1, no; (13), superior temporal sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (14), inferior temporal sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (15), lunate sulcus: 0, absent and 1, present; (16), size of cerebellar vermis relative to cerebellar hemisphere: 0, large and 1, small.
