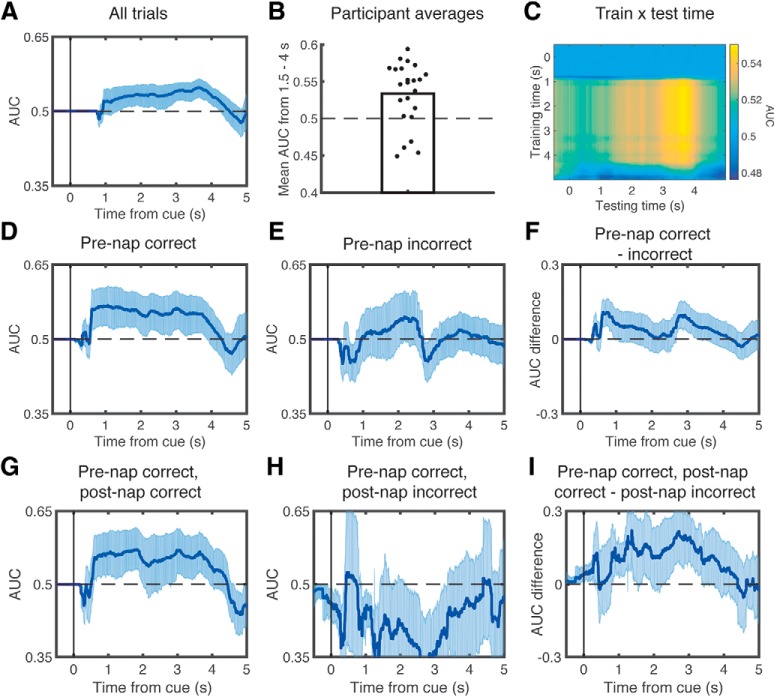
Figure 3.
Lateralized retrieval of learning content during sleep related to prenap and postnap memory. Using the lateralized components that discriminated left versus right motor imagery during wake as features, we trained a leave-one-subject-out classifier on sleep data and computed AUC-based classification performance time-locked to TMR cues. We found significant classification performance when using all trials (A). B, Significant across-subject decoding from 1.5 to 4 s. C, Performance when crossing training and testing time. We also found significant classification performance when focusing just on trials that were remembered prenap (D), but not for trials that were not remembered prenap (E). However, there were no significant differences in classification performance between these conditions (F). Using only trials that were remembered before the nap, we then found significant classification performance for trials that were subsequently remembered postnap (G), but not for those forgotten postnap (H), and there were significant differences in classification performance between these conditions (I). In all graphs, classification was performed on time-averaged signals within 1000 ms windows centered on each time point. Error bars indicate the edges of the middle 95th percentile of classification accuracies.