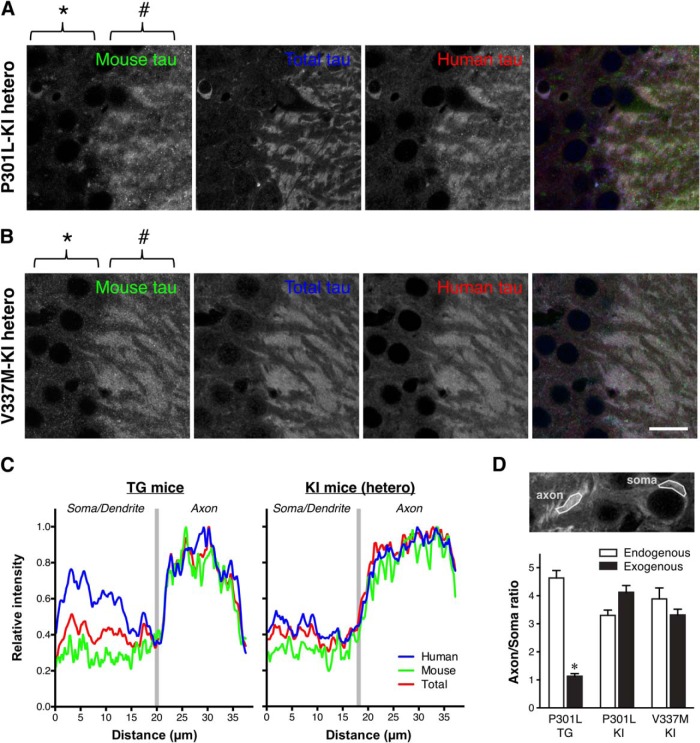
Figure 5.
Normal axonal localization of exogenous human tau in P301L tau knock-in mice. A, Mouse and human tau in the hippocampal CA3 of heterozygous P301L-KI mice were immunolabeled with anti-mouse tau (RTM47 shown in green), anti-total tau (tauN in blue), and anti-human tau (tau12 in red). It should be noted that, unlike in P301L-Tg mice, both mouse and human tau were virtually absent in the somata (*) but abundant in the axons (#). Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Mouse and human tau in the hippocampal CA3 of heterozygous V337M-KI mice immunolabeled as in A. Scale bar, 20 μm. C, Normalized intensity profiles of RTM47, anti-tauN, and tau12 in P301L-Tg and V337M-KI mice along lines drawn from the CA3 pyramidal cell layer (Soma/Dendrite) to mossy fiber (Axon) are shown. D, To quantify the difference in tau localization between Tg and KI mice, the axon/soma ratio of fluorescence intensity was computed and compared (see Materials and Methods). Endogenous mouse tau exhibited high ratios indicating its enrichment in the axon in both mouse models. In contrast, the exogenous human tau in P301L-Tg mice showed significantly lower ratios than those of endogenous mouse tau in the same animals (t(10) = 13.87, p < 0.0001 using repeated-measures two-way ANOVA and Sidak test) and exogenous human tau in P301L-KI mice (t(20) = 7.012, p < 0.0001) and in V337M-KI mice (t(20) = 5.287, p = 0.0002).