Figure 6.
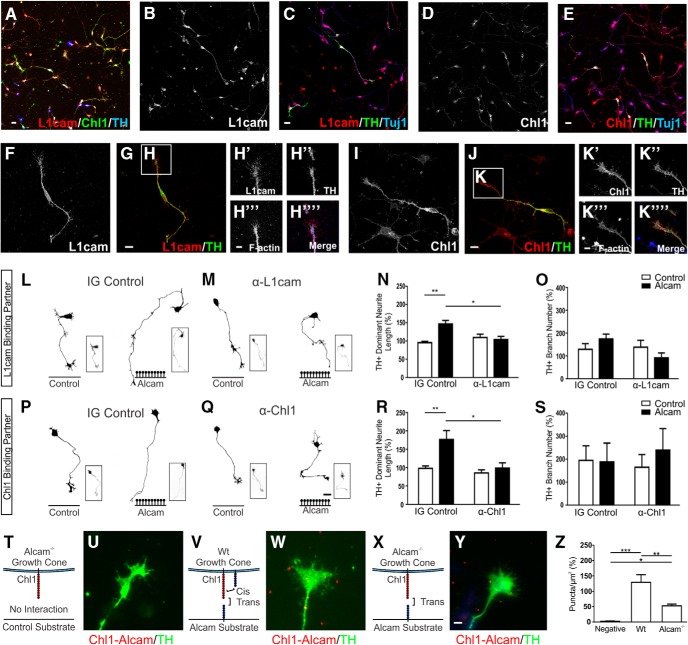
Functional analysis of Alcam trans-heterophilic interactions with the potential binding partners L1cam and Chl1. Representative images of primary midbrain cultures immunolabeled for the potential Alcam trans-heterophilic binding partners L1cam and Chl1 show broad expression of both CAM's in dopaminergic and nondopaminergic neurons (A). Expression was localized throughout the cell body, axons, and branches of all neurons for L1cam (B,C), and Chl1 (D,E). In dopaminergic neurons, L1cam expression was evenly distributed in cell bodies, axons (F,G), and F-actin+ growth cones (H). Parallel images of the potential Alcam-binding partner Chl1 (I,J) also show Chl1 expression in cell bodies, axons, and F-actin+ growth cones (K). Representative dopaminergic (TH+) neuron traces of WT neurons cultured on control or Alcam substrate in the presence of an IG control (L) or L1cam-neutralizing antibody (M), blocking potential trans heterophilic interactions between Alcam and L1cam. A significant interaction (two-way ANOVA, F(1,8) = 9.264, p = 0.0160) blocking antibody (F(1,8) = 6.531, p = 0.0339) and substrate (F(1,8) = 17.18, p = 0.0032) effect was detected (n = 3). The significant growth promoting effect of Alcam substrate on neurite length (N) (t = 5.083, df = 8, p = 0.0019) was ablated in the presence of functional blocking of L1cam (t = 0.7783, df = 8, p = 0.7071). Neurite length decreased significantly in a direct comparison of neurons grown on Alcam substrate in control and in the presence of the L1cam blocking antibody (t = 3.959, df = 8, p = 0.0248). No significant effect on branch number (O) was observed. Representative dopaminergic neuron traces of WT neurons cultured on control or Alcam substrate in the presence of IG control (P) or Chl1-neutralizing antibody (Q), blocking potential trans heterophilic interactions between Alcam and Chl1. A significant interaction (two-way ANOVA, F(1,8) = 5.650, p = 0.0447) blocking antibody (F(1,8) = 10.52, p = 0.0118) and substrate (F(1,8) = 9.549, p = 0.0149) effect was detected (n = 3). The significant growth promoting effect of Alcam substrate on neurite length (R) (t = 3.866, df = 8, p = 0.0095) was ablated in the presence of functional blocking of Chl1 (t = 0.5042, df = 8, p = 0.8614). Neurite length decreased significantly in a direct comparison of neurons grown on Alcam substrate in control and in the presence of the Chl1 blocking antibody (t = 3.975, df = 8, p = 0.0243). No significant effect on branch number (S) was observed. Representative immunohistochemistry images of primary dopaminergic growth cones immunolabeled using an in situ proximity ligation assay to detect interactions between Alcam and Chl1. Puncta (shown in red) indicate positive Alcam-Chl1 interactions in Alcam−/− neurons grown on a control substrate (T, U, no cis or trans interactions), WT neurons cultured on Alcam substrate (V, W, cis and trans interactions) and Alcam−/− neurons grown on an Alcam substrate (X, Y, trans interactions only). Quantification of Alcam-Chl1+ puncta (Z) showed a significant difference between groups (one-way ANOVA, F(2,8) = 27.00, p = 0.0003, n = 3–4). Relative to the negative control group, a significant increase in puncta was observed in WT neurons grown on Alcam substrate (t = 10.38, df = 8, p = 0.0002) and in Alcam−/− neurons grown on Alcam substrate (t = 4.420 df = 8, p = 0.0338). Comparison of WT and Alcam−/− neurons on Alcam substrate resulted in a significant 40% reduction in puncta (t = 46.291, df = 8, p = 0.0054) attributable directly to Alcam-Chl1 trans heterophilic interactions. Scale bars: A–E, 20 μm; F, G, 10 μm; H, 5 μm; I, J, 10 μm; K, 5 μm; L, M, P, Q, 20 μm; U, W, Y, 5 μm. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.