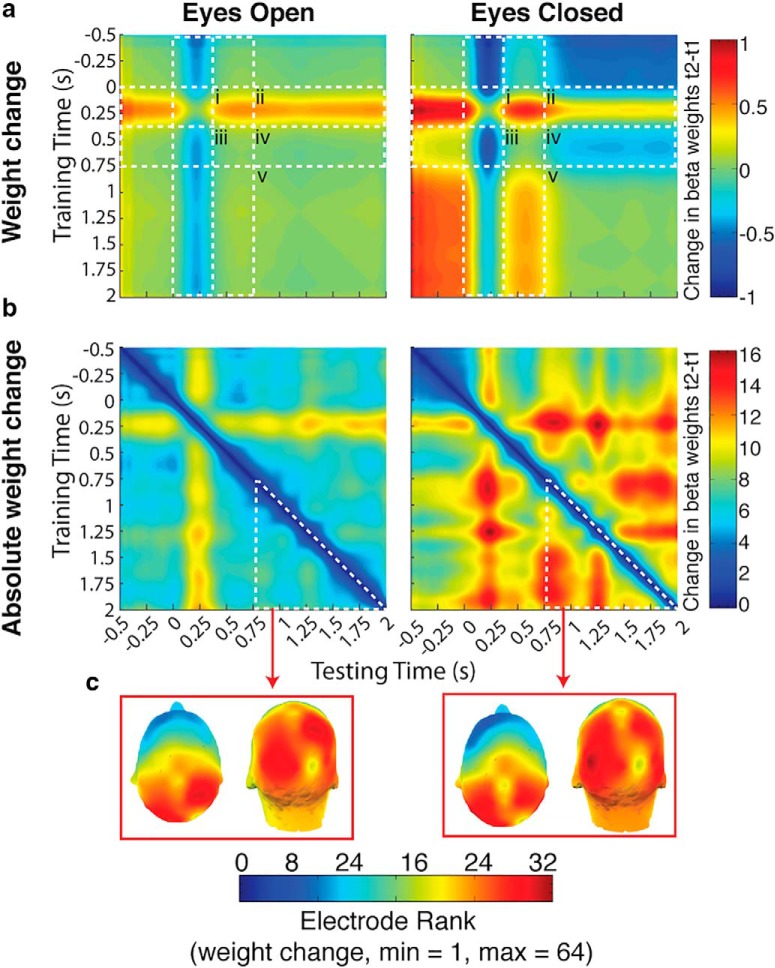
Figure 8.
Investigation into the nature of the weight change. a, In the eyes open condition, average weight change was ~0 throughout the retention interval (iii–v), following the initial average increase in weights from 250 ms after stimulus onset forward in time (i and ii). This same increase in weights was also present in the eyes closed condition (i and ii). However, there was an additional average change unique to the eyes closed condition: a decrease from around the time of eye closure (~300 to 750 ms after stimulus onset) forward into the rest of the retention interval (iv). Otherwise average weight change in the eyes closed condition was ~0 (iii and v). b, Weights were more dynamic throughout the trial in the eyes closed condition, including before eye closure, than in the eyes open condition. c, Changes in the eyes closed condition after eye closure, although greater than that during the same time period in the eyes open condition, are largely in parietal and occipital electrodes as they are in the eyes open condition.