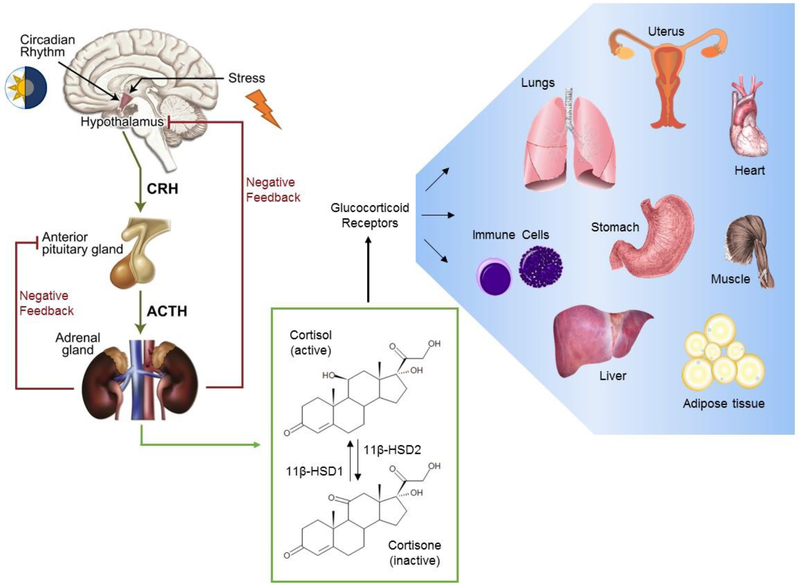
Figure 2:
Systemic and tissue-level regulation of glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoid synthesis is regulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, comprised of stimulatory and negative feedback signals which control the secretion of corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus, adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary gland and finally cortisol from the adrenal glands. The 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (11β-HSD) enzyme system is responsible for the activation and deactivation of cortisol, which in part is responsible for local regulation of cortisol. Cortisol induces its pleiotropic influences on peripheral tissues through glucocorticoid receptor-mediated actions, supporting the normal physiology and functioning of these organ systems. Figure adapted from Cruz-Tropete et al. [34, 51] and Oakley et al. [52].