Fig. 5.
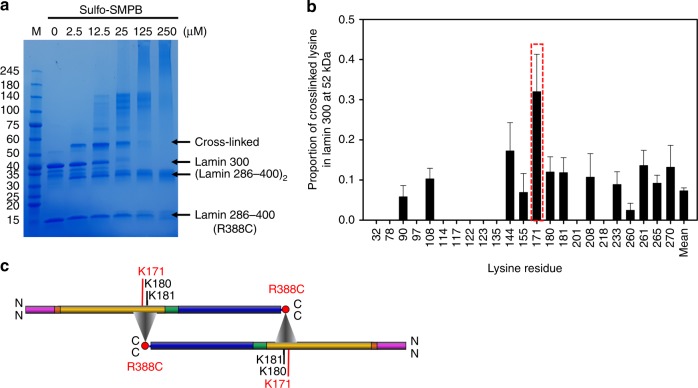
The eA22 interaction mapping by MS/MS analysis with cross-linked proteins. a The chemical cross-linking assay with the lamin 300 fragment and lamin 286–400 R388C mutant in SDS-PAGE. Protein bands of the lamin 300 fragment and the cross-linked sample are labelled. To block the unreacted chemical cross-linker, excess cysteine was added. The major bands of ‘cross-linked’ (52 kDa), lamin 300 (38 kDa), dimerized lamin 286–400 R388C [(lamin 286–400)2; 30 kDa], and lamin 286–400 R388C (14 kDa) were excised and subjected to the subsequent MS/MS analysis (Supplementary Data 1). b Proportion () of the Cys388-bound lysine residues at each position was determined by dividing the number of Cys388-bound lysine residues by the total number of observed lysine residues in the pooled data of cross-linked bands. Position of the most probable Lys171 to be cross-linked to Cys388 is shown in a red box in the plot. The error bars indicate each standard error of proportion, which were calculated by . See also Supplementary Table 2. c Schematic representation of the central rod domains of two coiled-coil dimers in the colour code of Fig. 1a, displaying the eA22 interaction based on the results of the MS/MS analysis. Triangles indicate that Arg388 (or Cys388) of coil 2 is around Lys171 (or its neighboring Lys180 or Lys181) of coil 1b in lamin 300 fragment