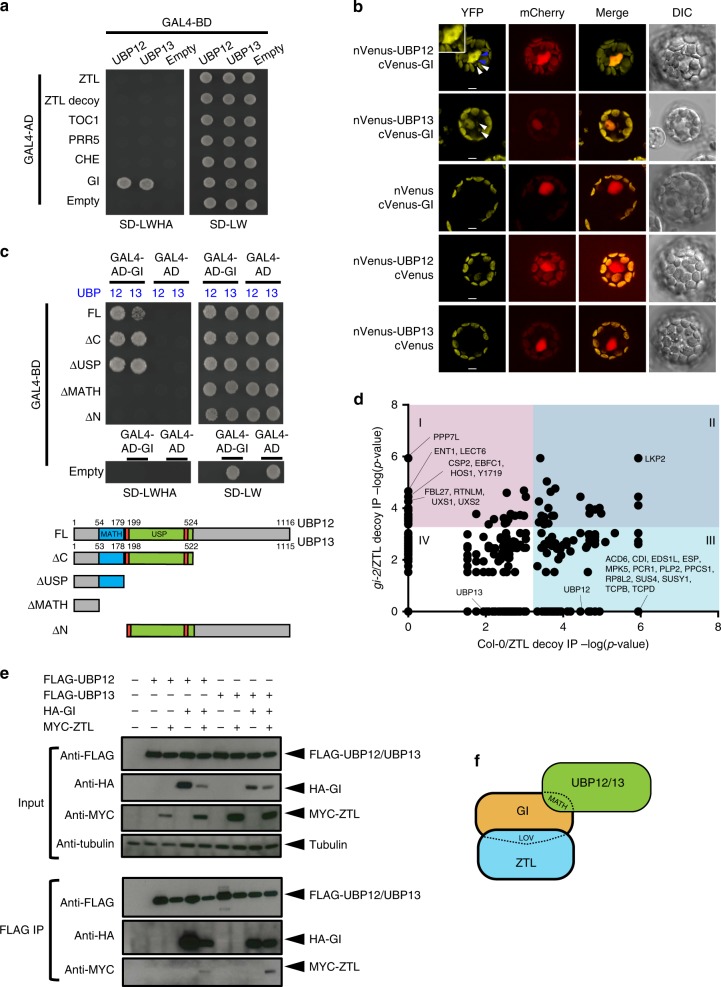
Fig. 1.
GI bridges the interactions between ZTL and UBP12 or UBP13. a Yeast two-hybrid showing interaction between GI and UBP12 or UBP13. The GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GAL4-BD) fused to UBP12 or UBP13 and either ZTL variants (ZTL and ZTL decoy), ZTL targets (TOC1, PRR5, and CHE) or GI fused to GAL4 activation domain (GAL4-AD) were grown on SD-LW medium for autotrophic selection and on SD-LWHA medium to test for interactions. b Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays to examine the interactions of UBP12 or UBP13 and GI fused to the N- or C-terminus of Venus (YFP) were performed in Arabidopsis protoplasts. The blue arrows indicate the interacting complex forming nuclear foci. The white arrows show fluorescence signal in the cytoplasm. mCherry-VirD2NLS was co-expressed as a nuclear marker, and the scale bar indicates 10 µm. c The protein domains of UBP12 and UBP13 required to interact with GI were tested using yeast two-hybrid assays. The full-length (FL) or truncated UBP12 or UBP13 fragments as diagramed in the lower portion of the panel were fused to GAL4-BD to test for interaction with GAL4-AD-GI. d Scatter plot of proteins identified by IP-MS of ZTL decoys in the Col-0 and gi-2 genotypes. The significance of the interactions were evaluated by SAINTexpress (see Methods and Supplementary Data 1 for complete information) with a false discovery rate (FDR) cutoff < 0.01 and p-value ≤ 5.37E-4 to separate interacting proteins into four groups. Group I: significant interactions with ZTL decoy in the gi-2 but not Col-0. Group II: significant interactions with ZTL decoy in both Col-0 and gi-2. Group III: significant interactions with ZTL decoy in the Col-0 but not gi-2. Group IV: Non-significant interactions with ZTL decoy in both Col-0 and gi-2. The interacting proteins significantly enriched in the gi-2 mutant over Col-0 were labeled along the y-axis, and the proteins enriched in the Col-0 over the gi-2 mutant were labeled along the x-axis. e Co-immunoprecipitation assays showing that UBP12 or UBP13 interact with ZTL in a GI-dependent manner. FLAG-UBP12 or FLAG-UBP13 were co-infiltrated with HA-GI and Myc-ZTL in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Anti-FLAG antibody was used to immunoprecipitate FLAG-UBP12 or FLAG-UBP13. Western blotting with anti-FLAG, anti-HA, or anti-Myc was used to detect the presence of FLAG-UBP12, FLAG-UBP13, HA-GI, or Myc-ZTL in the immunoprecipitated samples and inputs. f The diagram depicts the interaction between GI and the MATH domain of UBP12 or UBP13, and between GI and the LOV domain of ZTL. The source data are provided as a Source Data file. Blot images were cropped from their original size, which can be found in Source Data file