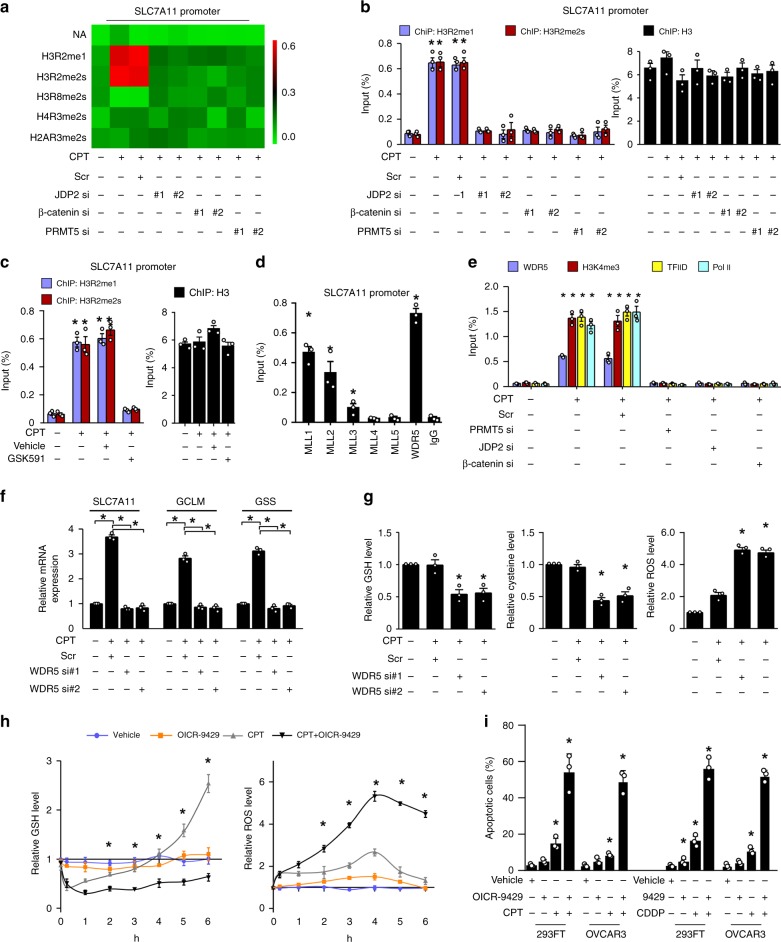
Fig. 6.
PRMT5-mediated histone H3R2 methylation contributes to genotoxic stress-induced GSH metabolism. a ChIP assay analysis of the enrichment of H3R2me1, H3R2me2s, H3R8me2s, H4R3me2s, and H2AR3me12s on the promoter of SLC7A11 in the indicated cells treated with CPT (10 μM, 1 h). The heatmap represented by pseudocolors was generated using the ChIP-qPCR values, arrayed from green (no enrichment) to red (maximal enrichment), to demonstrate the histone methylarginine code surrounding the promoter of SLC7A11. b, c ChIP assay analysis of the enrichment of H3R2me1 and H3R2me2s on the promoter of SLC7A11 in the indicated cells treated with CPT (10 μM, 1 h) (b) or PRMT5 inhibitor GSK591 (5 μM, 1 h) (c). ChIP-qPCR of Histone 3 served as the control. d, e ChIP assays analyses of enrichment of MLL1, MLL2, MLL3, MLL4, MLL5, and WDR5 (d) or WDR5, H3K4me3, transcriptional factor IID (TFIID), and polymerase II (e) on the promoter of SLC7A11 in CPT (10 μM, 1 h)-treated cells. Anti-IgG antibody served as the control. f Relative mRNA expression of SLC7A11, GCLM, and GSS in the scramble- or WDR5 siRNA(s)-transfected cells treated with or without CPT (10 μM, 1 h), as quantified by qRT-PCR analysis. GAPDH serve as the loading control. g Relative expression levels of GSH (left), cysteine (middle), and ROS (right) were examined in scramble- or WDR5 siRNA(s)-transfected cells treated with or without CPT (10 μM, 4 h). h Relative levels of GSH (left) and ROS (right) in vehicle-, or OICR-9429 (a WDR5 inhibitor, 5 μM, 4 h)-, or CPT (10 μM, 4 h), or OICR-9429 (10 μM, 4 h) plus CPT (10 μM, 4 h)-treated cells at the indicated times. i Quantification of the apoptotic index in the indicated cells treated with vehicle-, or OICR-9429 (10 μM)-, or CPT (10 μM), or OICR-9429 (10 μM) plus CPT (10 μM), as analyzed by an Annexin-V assay. + : treatment, −: untreatment. Each error bar in panels a–i represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. Student's two-tailed t test. Source data of Fig. 6b–i are provided as a Source Data file