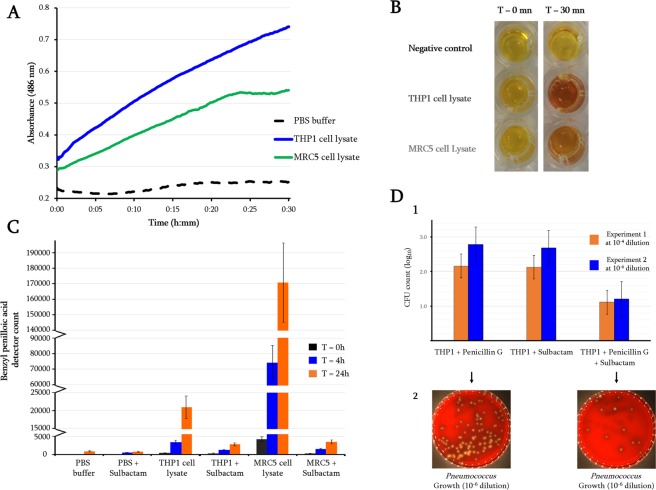
Figure 1.
Beta-lactamase activity detected in human cell cultures. (A) Spectrophotometric assay of nitrocefin degradation in the presence of THP1 and MRC5 cell lysates monitored for 30 minutes by monitoring absorbance at 486 nm; (B) Nitrocefin solutions with added THP1 and MRC5 cell lysates or PBS (used as negative control), incubated at 25 °C and observed after 30 minutes. The appearance of a red-coloured product indicates positive β-lactamase activity, while a constant yellow colour indicates no activity; (C) LC/MS average detector counts of metabolite benzyl penilloic acid monitored during 24 hours. Penicillin G was added in the presence of human cell lysates (THP1 and MRC5) in the presence or absence of sulbactam; (D) determination of the growth of highly penicillin-susceptible Pneumococcus within human THP1 cells in the presence of penicillin G or sulbactam alone, and in the presence of both. (D1) CFU count (log10) of the Pneumococcus strain under the three different conditions after 24 h incubation in THP1 cells. (D2) Bacterial colonies resulting from THP1 cell lysis grown on agar plates and observed after 24 hours. The Pneumococcus strain grew more easily within THP1 cells, despite the presence of penicillin G, than when sulbactam was added.