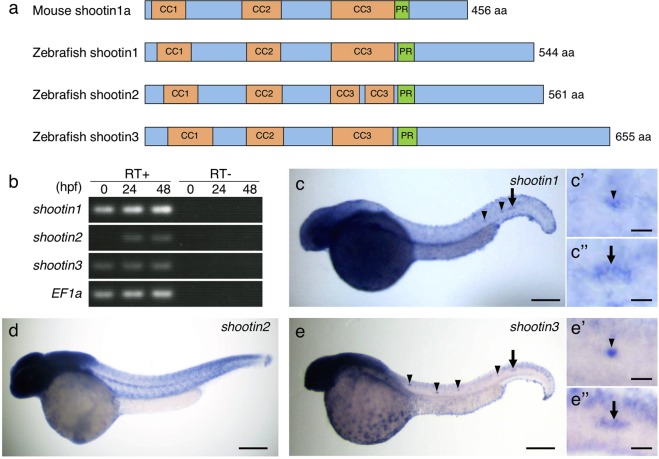
Figure 1.
Identification and expression of zebrafish shootin genes. (a) Schematic representation of zebrafish shootin1, shootin2, shootin3 and mouse shootin1 protein structures. The top box for mouse shootin1 indicates the structural domains described previously26, and the bottom three boxes for zebrafish shootin1, shootin2 and shootin3 indicate the corresponding structural domains. CC1-3, coiled-coil domains 1–3; PR: proline-rich domain. (b) RT-PCR analysis of shootin1, shootin2 and shootin3 transcripts. Elongation factor 1a (EF1a) was used as a control. Developmental stages are denoted in hours post-fertilization (hpf). RT-PCR products produced in the presence (RT+) or absence (RT−) of reverse transcriptase were electrophoresed using a 3% agarose gel. (c–e) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of shootin1 (c), shootin2 (d) and shootin3 (e) in zebrafish embryos at 36 hpf. Arrowheads and arrows indicate neuromasts and PLLP, respectively. Enlarged images indicate expression of shootin1 and shootin3 in the last deposited neuromasts (c’ and e’) and the PLLP (c” and e”). Scale bars: 200 μm for whole body images and 25 μm for enlarged images.