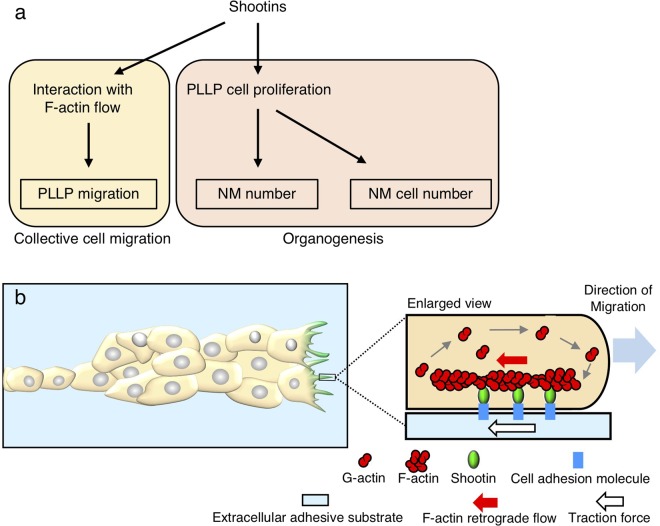
Figure 6.
A working model for how shootins mediate collective cell migration and organogenesis of the zebrafish posterior lateral line system. (a) A model for shootin-mediated collective cell migration and organogenesis of the zebrafish posterior lateral line system. Shootins mediate PLLP migration through its interaction with F-actin at the leading edge of the leader cells. Shootins promote cell proliferation in the PLLP, thereby positively regulating the number of neuromasts and the number of cells in the deposited neuromasts. (b) A mechanistic model for shootin1-mediated zebrafish PLLP migration. F-actins polymerize at the filopodia and lamellipodia of PLLP leading cells and depolymerize proximally, thereby inducing retrograde flow of F-actins (red arrow). Shootin1 couples mechanically the F-actin retrograde flow and extracellular adhesive substrates, thereby transmitting the force of F-actin flow (red arrow) to the substrates as a traction force (white arrow)31,32,34. The driving force for PLLP migration (blue arrow) is produced as a counterforce to the traction forces exerted on the extracellular substrates (white arrow).