Figure 3.
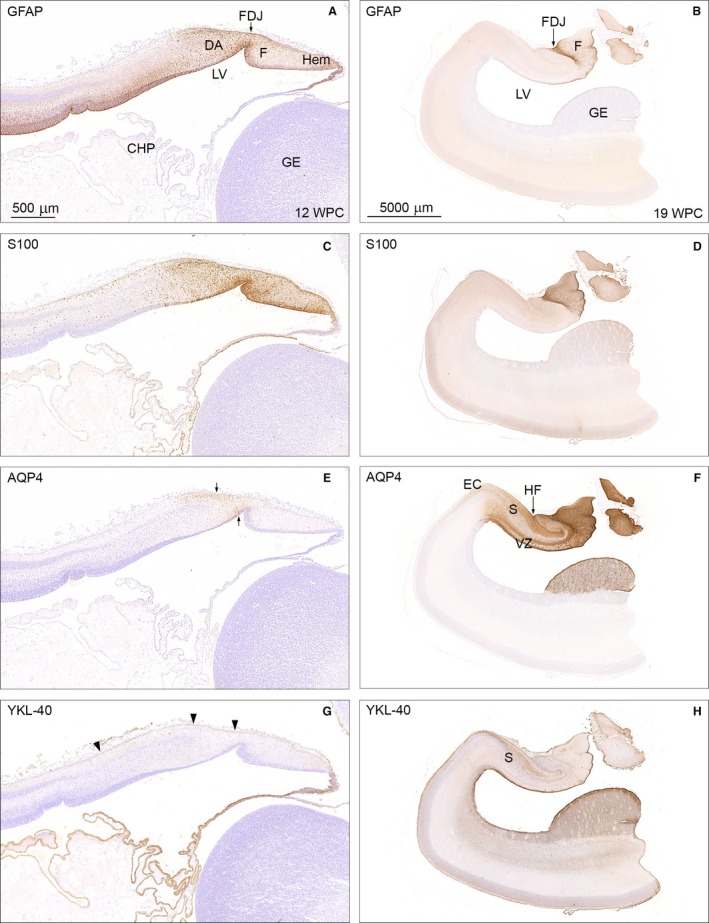
Temporal patterns of GFAP, S100, AQP4 and YKL‐40 immunoreactivity in 12 wpc (CRL: 74 mm) and 19 wpc (CRL: 165 mm) human fetal brain. Panel 1 (A,C,E,G) shows higher magnification of the framed areas in Figs 2A and B and of neighboring sections from the same 12 wpc fetus stained for AQP4 and YKL‐40. Panel 2 (B,D,F,H) illustrates the same region from a 19 wpc coronally sectioned fetus stained for the same astroglial markers: GFAP, S100, AQP4 and YKL‐40. At 12 wpc (panel 1) GFAP‐ and S100 immunoreactivity in (A) and (C) of the fimbria (F) and the dentate anlage (DA) separated by the fimbriodentate junction (FDJ) is strong but not entirely overlapping. In the marginal zone, S100‐reactivity continues into the hippocampus proper, which is devoid of GFAP staining. AQP4 and YKL‐40 immunoreactivity in (E) and (G) depicts the upcoming AQP4‐positive radial glial fibers in the DA between small arrows in (E) and the YKL‐40‐positive radial glial end feet (arrowheads) in (G). At 19 wpc the FDJ is strongly immunoreactive for GFAP (B), S100 (D) and AQP4 (F) but not for YKL‐40 (H). CHP, choroid plexus; DA, dentate anlage; EC, entorhinal cortex; F, fimbria; FDJ, fimbriodentate junction; GE, ganglionic eminence; Hem, hem; HF, hippocampal fissure; LV, lateral ventricle; S, subiculum; VZ, ventricular zone. Panel 1 (A, C, E and G) – same magnification, scale bar in (A): 500 μm. Panel 2 (B,D,F,H) – same magnification. Scale bar: (B) 5000 μm.
