Figure 4.
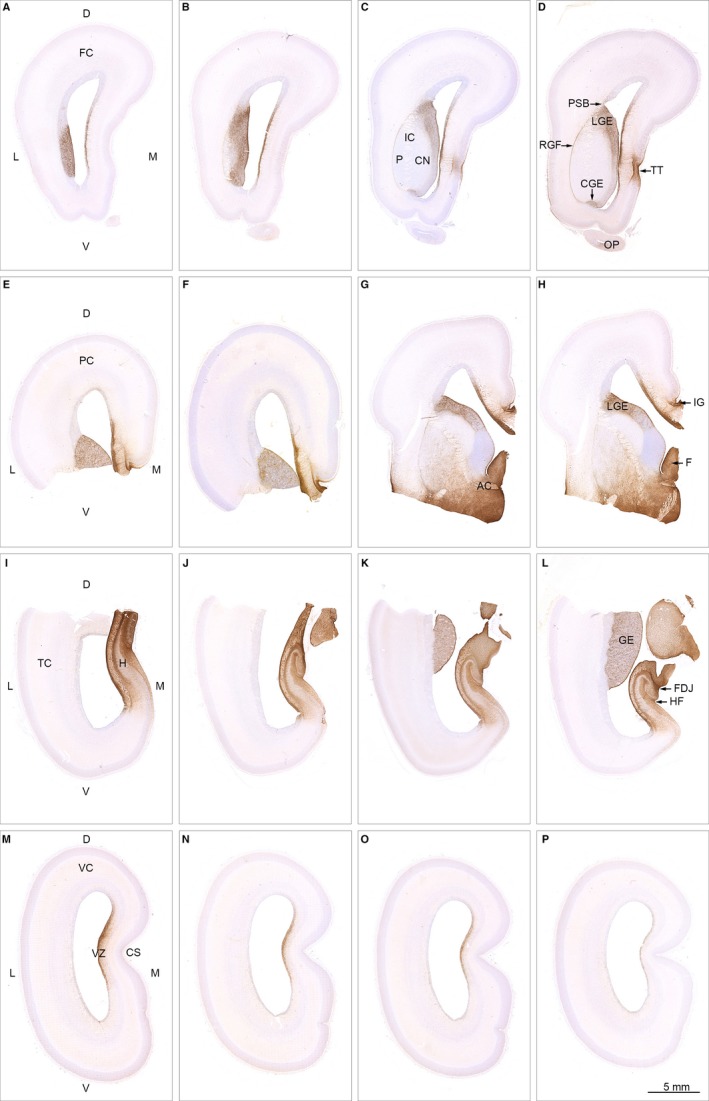
Spatial distribution of AQP4 in 19 wpc (CRL: 165 mm) human fetal brain. Sixteen sections immunostained for AQP4 from a series of more than 4000 coronal sections through the entire brain of a 19 wpc human fetus and taken from the material shown in Box 1 C (A–D from frontal lobe; E‐H from parietal lobe; I‐L from temporal lobe; M‐P from occipital lobe). At 19 wpc, APQ4 immunoreactivity delineates a continuous water transport system from the hippocampal formation (H) in (I) to taenia tecta (TT) in the medial frontal cortex (D) and via the basal forebrain (G,H) to the ganglionic eminence. The ventricular zone (VZ in M) of the medial wall also shows a continuous labeling from frontal to occipital lobe. The olfactory peduncle (OP in D) is weakly stained at this stage. Orientation: D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral. The entire cortical wall: FC, frontal cortex; PC, parietal cortex; TC, temporal cortex; VC, visual cortex. Subregions: AC, anterior commissure; CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; CN, caudate nucleus; CS, calcarine sulcus; FDJ, fibriodentate junction; GE, ganglionic eminence; RGF, radial glia fiber fascicle; H, hippocampus; HF, hippocampal fissure; IC, internal capsule; IG, indusium griseum; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; OP, olfactory peduncle; PSB, pallial–subpallial boundary; TT, taenia tecta; VZ, ventricular zone. A‐P: same magnification. Scale bar: (P) 5 mm.
