Figure 6.
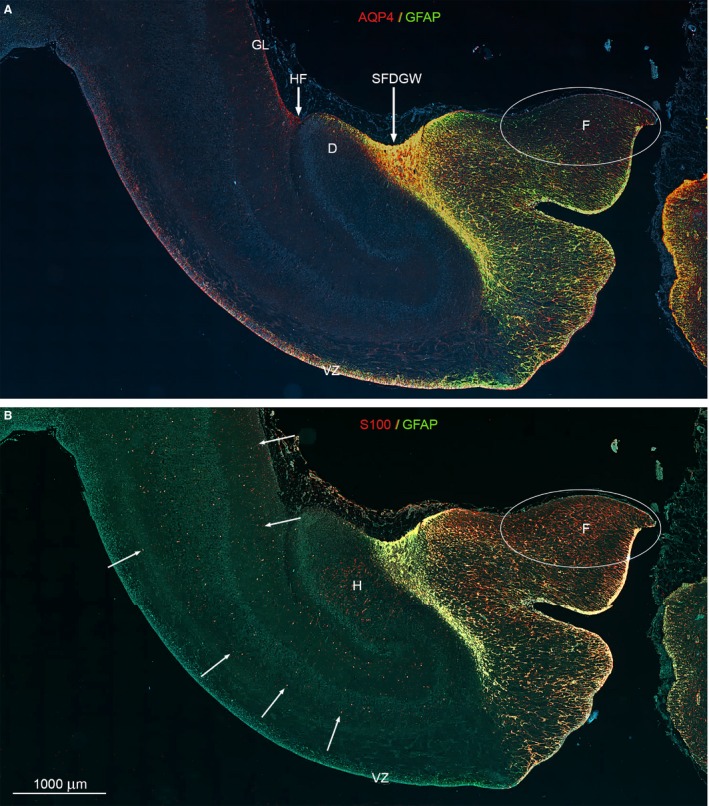
Whole‐slide fluorescent scanning of hippocampal formation from 19 wpc human fetal brain. Two immunofluorescent consecutive sections double‐labeled with antibodies against AQP4 and GFAP (A) and S100 and GFAP (B). Both sections are from the hippocampal formation adjacent to the bright‐field AQP4‐immunostained section shown in Fig. 5. (A, B) Include the entire wall of the hippocampal formation with the subpial fimbriodentate gliogenic wedge (SFDGW) region at the fimbriodentate junction and subiculum in the upper left corner – compare with Fig. 3F. The double‐labeled sections with DAPI‐stained nuclei shown in blue were subjected to whole‐slide fluorescent scanning. Radial glial cells in the ventricular zone (VZ) of the entire HF including the most distal part of fimbria is strongly positive for AQP4 as shown by the red and yellow color in (A). Within the cerebral wall, a diffuse fine dotted reactivity for AQP4 (red) can be distinguished in (A) (see also Fig. 3F) as opposed to the evenly distributed marked cellular S100 reactivity (red) indicated with white arrows in (B). The ventricular zone and the underlying future alveus are not labeled but there is an accumulation of S100‐positive cells in the hilus (H) of the dentate (D). (A, B) The subpial fimbriodentate gliogenic wedge (SFDGW) exhibits very strong immunoreactivity for the astroglial markers AQP4, GFAP and S100 and is mainly yellow with overlap, but also shows specific red (AQP4) patches in (A) and green (GFAP) patches in (B). D, dentate; F, fimbria; GL, glia limitans; H, hilus; HF, hippocampal fissure; SFDGW, subpial fimbriodentate gliogenic wedge; VZ, ventricular zone. (A–B) – same magnification. Scale bar: (B) 1000 μm.
