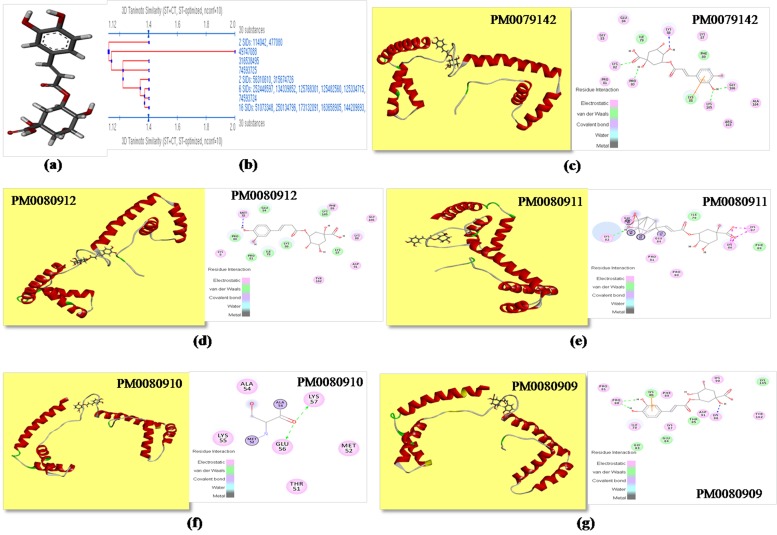
Figure 3.
(a) Structure of chlorogenic acid used as a ligand for molecular docking (CID-1794427); (b) Identification of CGA conformers by structure clustering approach; (c) Molecular Docking of CGA with mice HMGB1 protein (PMDBID: PM0079142) and representation of active site residues and force of attractions involved in docking; (d) Molecular Docking of conformer C3950 with mice HMGB1 protein (PMDB ID: PM0080912) and representation of active site residues and force of attractions involved in docking; (e) Molecular Docking of conformer ZINC03947476 with mice HMGB1 protein (PMDB ID: PM0080911) and representation of active site residues and force of attractions involved in docking; (f) Molecular Docking of conformer iso-chlorogenic acid with mice HMGB1 protein (PMDB ID: PM0080910) and representation of active site residues and force of attractions involved in docking; (g) Molecular Docking of conformer cis-chlorogenic acid with mice HMGB-1 protein (PMDB ID: PM0080909) and representation of active site residues and force of attractions involved in docking.