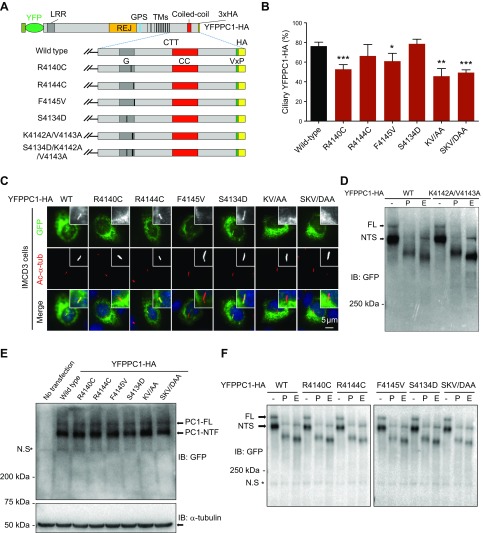
Figure 5.
Ciliary targeting of full-length PC1 is compromised by mutations that affect PC1-PP1 binding. A) Schematic representation of full-length YFPPC1-HA and various point mutant variants. B) Respective constructs in A were individually expressed in IMCD3 cells. Ciliary expression of these constructs was evaluated by staining with antibody against GFP (green), and cilia were marked with acetylated α-tubulin (Ac-α-tub; red). Representative images of each construct to function are shown. Scale bar, 5 μm. C) Quantification of percentage of YFPPC1-HA–positive cilia in cells. A total of ≥50 ciliated, PC1-transfected cells were counted for the presence of the YFPPC1-HA signal on cilia under each condition. Error bars represent the sd between microscope fields from ≥3 independent experiments. D) Deglycosylation analysis of YFPPC1-HA WT or K4142A/V4143A mutant exogenously expressed in HEK293 cells. Representative blots are shown from 3 independent experiments. E) Western blots of recombinant PC1 expressed in HEK293 cells, PC1 was detected using an antibody against GFP, and α-tubulin was used as loading control. NTF, N-terminal fragment. F) Deglycosylation analysis of WT and mutant full-length PC1. All constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells, and cell lysates were incubated with either reaction buffer alone (−), peptide:N-glycosidase F (P), or endoglycosidase H (E) and detected with an antibody against GFP. CC, coiled-coil domain; FL, full-length; G, G-protein activation domain; IB, immunoblot; KV/AA, K4142A/V4143A; SKV/DAA, S4134D/K4142A/V4143A; LRR, leucine-rich repeat; NTS, N-terminal fragment, endoglycosidase H sensitive; N.S, non-specific band; REJ, receptor for egg jelly; TMs, transmembrane domains. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with WT control.