Figure 4.
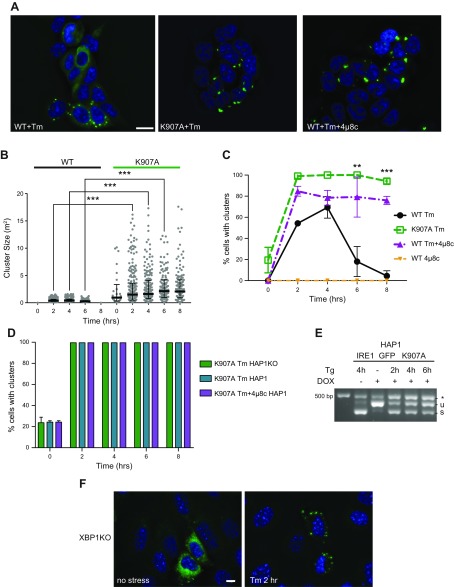
A functional IRE1α RNase domain is not needed for cluster formation but affects cluster dispersal. A) RNase-inhibited IRE1α still clusters. HAP1KO cells expressing K907A or WT IRE1GFP were induced with dox and treated with either Tm for 2 h, or 4μ8C (16 μM) plus Tm for 2 h. Representative pictures are shown. B) Clusters of K907A are bigger than WT IRE1GFP clusters. Histogram distribution of cluster size (square micrometers) following Tm treatment at the indicated times. At least 119 cells were evaluated for each condition. ***P < 0.001. C) RNase-inhibited IRE1α displays persistent clustering. Percentages of K907A or WT IRE1GFP cells that clustered following Tm (4 μg/ml), 4μ8c (16 μM), or Tm (4 μg/ml) plus 4μ8c (16 μM) treatments were graphed. At least 291 cells were evaluated for each condition. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. D) Hyperclustering is intrinsic to K907A IRE1α. HAP1KO cells or parental HAP1 cells, which expressed K907A IRE1GFP were induced with dox, treated with Tm or with Tm plus 4μ8c, as in C. The percentages of cells with clusters are graphed. E) K907A IRE1α affects WT IRE1α XBP1 splicing. Parental HAP1 cells expressing K907A IRE1GFP were treated with Tg (0.2 μM) for the indicated times and XBP1 mRNA splicing was determined by RT-PCR. F) Absence of the XBP1 gene does not affect the ability of IRE1α to cluster. XBP1KO MEFs were transiently transfected with WT IRE1GFP and TetON plasmids and induced with dox as before. The cells were then treated with Tm (4 μg/ml) and imaged at 0 and 2 h. Representative pictures are shown. The exposure time for GFP was 1 s. Scale bars, 10 μm.