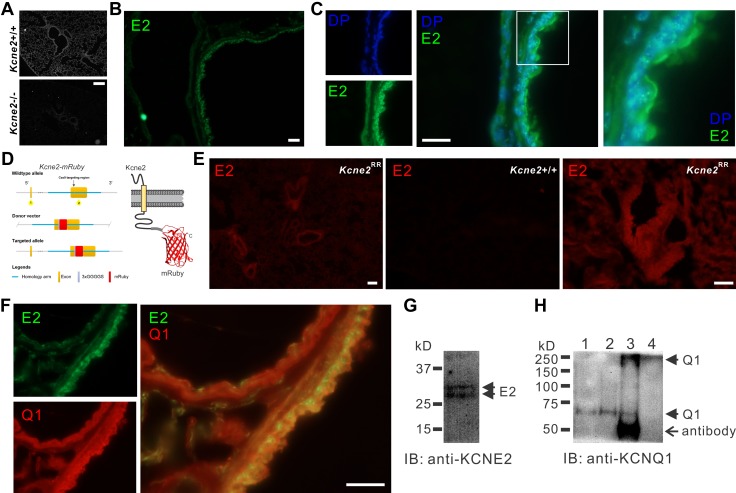
Figure 2.
Kcne2 colocalizes with Kcnq1 in mouse lungs. A) Immunofluorescence detection of Kcne2 protein in Kcne2+/+ but not Kcne2−/− mouse lung tissue. Scale bar, 40 µm. B) Immunofluorescence detection of Kcne2 (E2) protein (green) in Kcne2+/+ mouse lung tissue. Scale bar, 10 µm. C) Immunofluorescence detection of Kcne2 protein (green) in Kcne2+/+ mouse lung tissue compared with location of the nucleus stained with DAPI (DP; blue). Left, single channel images; center, merged; right, close-up images of boxed region from center panel. Scale bar, 10 µm. D) Schematic of CRISPR/Cas9 targeting approach to generate Kcne2RR mice. E) Fluorescence detection of Kcne2-mRuby (red) in Kcne2RR but not Kcne2+/+ mouse lung tissue. Scale bars, 20 µm. F) Immunofluorescence detection of Kcne2 protein (green) and Kcnq1 protein (Q1) (red) in Kcne2+/+ mouse lung tissue. Left, single channel images; right, merged. Scale bar, 10 µm. G) Western immunoblot (IB) of Kcne2 in mouse lung lysate. H) Anti-Kcnq1 Western IB showing detection of Kcnq1 from mouse lung lysates immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Kcne2 antibody. Lanes: 1, lysate; 2, anti-Kcnq1 IP; 3, anti-Kcne2 IP; 4, supernatant after initial bead precipitation from anti-Kcne2 IP. Kcnq1 bands at MWs corresponding to both the monomeric (60-kD) and the tetrameric (240-kD) forms are visible in the anti-Kcne2 lane (lane 3). No Kcnq1 was detectable in the supernatant after the Kcne2 IP (lane 4).