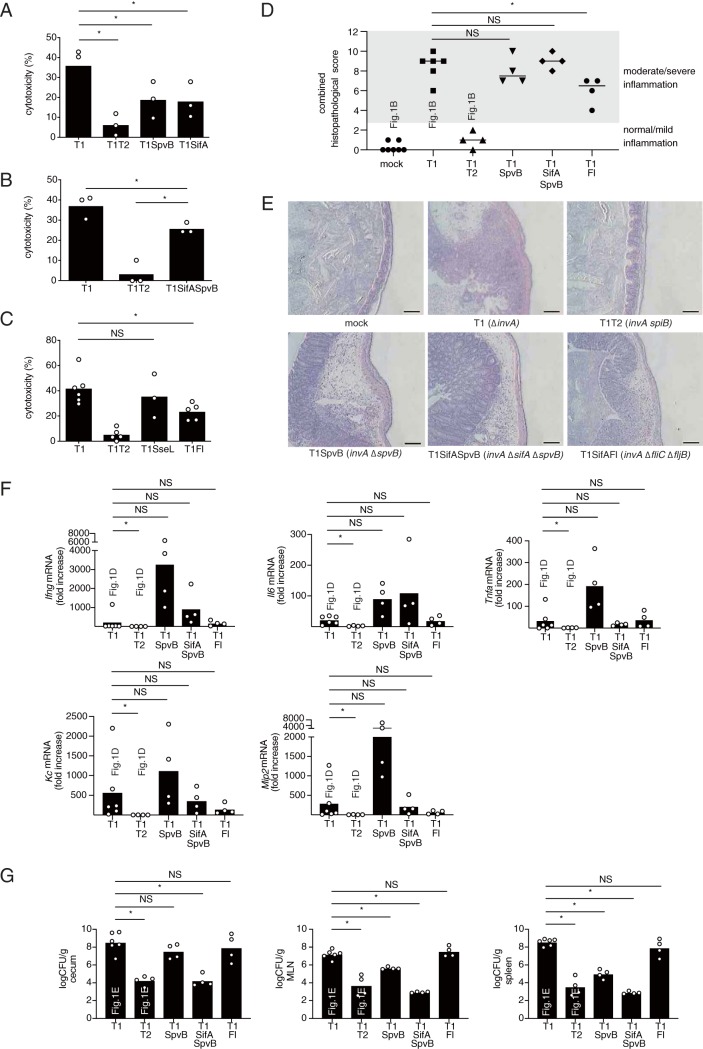
FIG 2.
The S. Typhimurium strains, T1SpvB, T1SifA, and T1Fl, that reduce the cytotoxicity of macrophages elicit T3SS-1-independent inflammation in mice. (A to C) LDH release from RAW cells infected with the indicated S. Typhimurium mutant strains at 20 h after infection. (D and E) Histopathology of the murine cecum 5 days after infection with the indicated S. Typhimurium mutant strains. The histopathology score was determined by the blinded examination of cecal sections. Each plot represents an individual mouse (D). Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained cecal sections are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm (E). (F) Transcript levels of Ifng, Il6, Tnfa, Kc, and Mip2 in the ceca of mice infected with the indicated S. Typhimurium strains at 5 days after infection, as measured by qPCR. (G) Numbers of bacteria recovered from the ceca, mesenteric lymph nodes and spleen of mice 5 days after infection. The combined histopathological score, the expression levels of genes, and bacterial numbers in the tissue of mice infected with invA (T1) or invA spiB (T1T2) were determined as shown in Fig. 1B, D, and E, respectively. The two-tailed Student t test (A to C) and the Mann-Whitney U test (E to G) were performed for statistical analysis. Individual data are shown as a scatter plot, and bars indicate the means. Asterisks indicate differences that were statistically significant (P < 0.05). NS, not significant.