Figure 5.
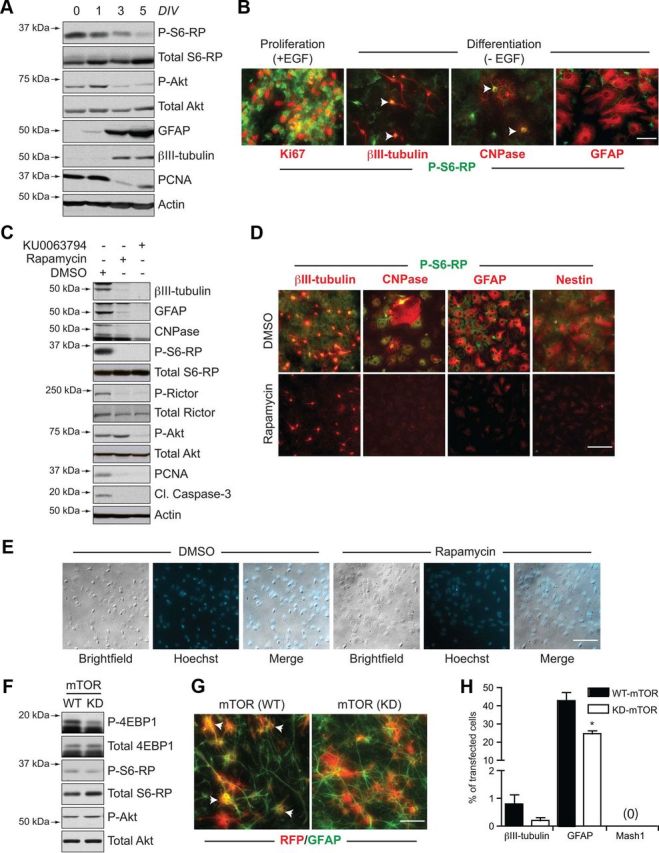
mTOR inhibition in the absence of EGF induces a quiescence-like phenotype in neurosphere cultures. A, B, Differentiation-induced changes in mTOR signaling. Western blot analysis of biochemical changes in adult neurosphere cultures differentiating from 0 to 5 d in vitro (DIV) (A), showing declining phosphorylation of S6-RP and Akt concomitant to generation of differentiated neurons (βIII-tubulin) and astrocytes (GFAP). B, Immunocytochemistry showing the reduction in P-S6-RP immunoreactivity following EGF withdrawal-induced differentiation. Whereas high levels of P-S6-RP immunoreactivity are present during EGF-induced proliferation (left), strong P-S6-RP is maintained in only βIII-tubulin+ neurons and CNPase+ oligodendrocytes during differentiation (arrows), while GFAP+ astrocytes are only weakly positive. C, D, mTOR inhibitors elicit a quiescence-like phenotype. C, Western blots showing biochemical changes in adult neurosphere cultures differentiated for 7 d in the presence of DMSO, rapamycin (20 nm), or KU0063794 (100 nm). Both mTOR inhibitors reduced expression of markers for proliferation (PCNA), differentiated neurons (βIII-tubulin), astrocytes (GFAP), and oligodendrocytes (CNPase), and eliminated phosphorylation of the mTORC1 targets S6-RP and Rictor. Only KU0063794 also blocked mTORC2-associated phosphorylation at AktSer473. D, Immunocytochemical changes in neurosphere cultures differentiated with DMSO versus rapamycin for 7 d. Rapamycin treatment decreased expression of markers for differentiated neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes, as well as the expression of the neural precursor marker Nestin (representative results from 1 of 4 independent experiments). E, Brightfield and fluorescent images of DMSO and rapamycin-treated cultures from D showing the absence of obvious morphological or nuclear signs of cell death, consistent with the inhibitor-induced reduction in cleaved caspase-3 in C. F, G, In vitro transfections with WT or KD forms of mTOR. F, Western blotting of lysates from HEK293 cells transfected for 2 d with mTOR(WT) or mTOR(KD) plasmids. Phosphorylation of 4-EBP1 and S6-RP are decreased by mTOR(KD). G, Immunocytochemistry for red fluorescent protein (RFP) and GFAP+ astrocytes following transfection of dissociated neurospheres and 6 d of differentiation (arrows identify double-labelled cells). H, Quantification following immunocytochemical analysis of transfected cells. Cells transfected with mTOR(KD) differentiate into fewer neurons and astrocytes and do not upregulate Mash1. Graph shows the mean and SEM from n = 4 independent experiments (200–400 transfected cells analyzed per marker per experiment). *p < 0.05. Scale bars: B, G, 50 μm; D, E, 25 μm.
