Figure 2.
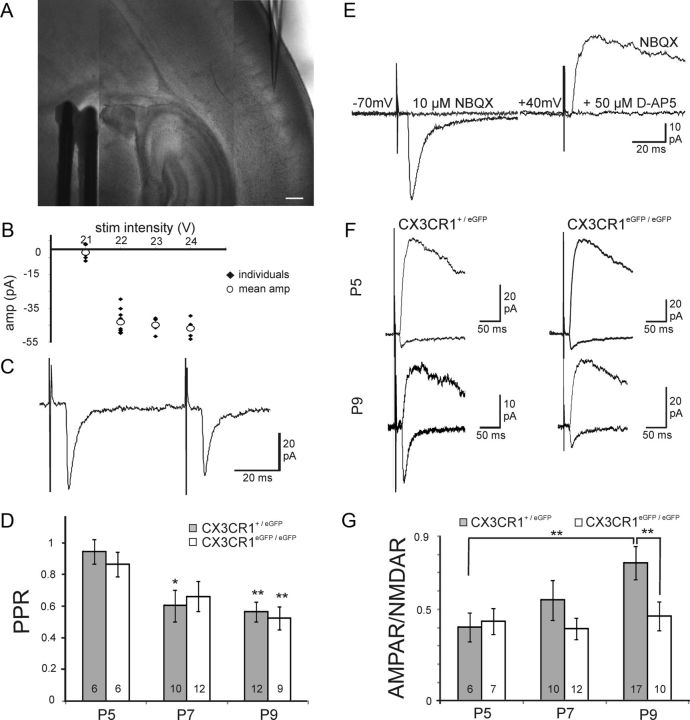
CX3CR1 deficiency impairs the functional maturation of thalamocortical synapses. A, DIC image of a P7 thalamocortical slice with the recording pipette in a barrel and the bipolar stimulating electrode in the internal capsule. Scale bar, 200 μm. B, Peak amplitude of individual (black dots) and mean (white circles) thalamocortical EPSCs plotted as a function of the stimulation intensity for the determination of the minimal stimulation (22 V in this example). C, Same cell as in B, thalamocortical EPSCs evoked by two stimulations for the determination of the paired-pulse ratio. D, Similar paired-pulse ratios of thalamocortical EPSCs in CX3CR1+/eGFP and CX3CR1eGFP/eGFP mice at P5, P7, and P9. Statistical differences between P5 and other ages within each genotype are indicated. E, Effect of NBQX and d-AP-5 on thalamocortical EPSCs evoked in a P9 neuron. F, AMPAR- and NMDAR-mediated EPSCs in layer 4 neurons of P5 and P9 CX3CR1+/eGFP and CX3CR1eGFP/eGFP mice. G, Comparison of the AMPAR/NMDAR ratio for P5, P7, and P9 CX3CR1+/eGFP and CX3CR1eGFP/eGFP mice. Each trace is an average of 15–20 individual sweeps. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (unpaired t test with Welch correction).